Modules:MedianFilter-Documentation-3.6
Return to Slicer 3.6 Documentation
Module Name
Median Image Filter
General Information
Module Type & Category
Type: CLI
Category: Filtering.Denoising
Authors, Collaborators & Contact
- Author: Bill Lorensen
- Contact: bill.lorensen at gmail.com
Module Description
The MedianImageFilter is commonly used as a robust approach for noise reduction. This filter is particularly efficient against 'salt-and-pepper' noise. In other words, it is robust to the presence of gray-level outliers. MedianImageFilter computes the value of each output pixel as the statistical median of the neighborhood of values around the corresponding input pixel.
Usage
Examples, Use Cases & Tutorials
- This module is used to reduce noise in an image. It is most effective in reducing additive salt-and-pepper noise without grossly shift the edge structures. It may, however, remove thin structures such as thin vessels when the "Neighborhood Size" is too big.
- A command line example of running this module is
MedianImageFilter --neighborhood 1,1,1 CTHeadAxial.nhdr MedianImageFilterTest.nhdr
Quick Tour of Features and Use
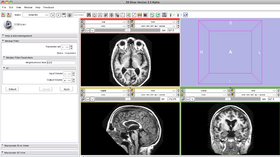
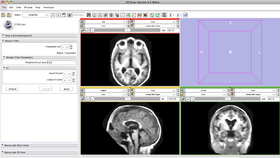
- Input/output panel:
User selects an image as input upon which the medial filter will apply. User creates an output image to store the result. Upon completion, the output image will be displayed in the viewing panel.
- Parameters panel:
User specifies the neighborhood radius in three dimensions (comma separated without spaces). The bigger the size, the smoother the resulting image and the poorer the fine structures are preserved.
- Viewing panel:
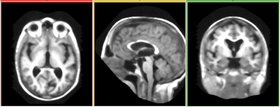
Upon completion, the median filter result is displayed in the viewing panel.
Development
Dependencies
None other than the core Slicer3 modules for image IO and display.
Known bugs
None.
Usability issues
None.
Source code & documentation
Source Code: MedianImageFilter.cxx
XML Description: MedianImageFilter.xml
Test: MedianImageFilterTest.cxx
Documentation:
USAGE:
./MedianImageFilter --help
./MedianImageFilter [--returnparameterfile <std::string>]
[--processinformationaddress <std::string>] [--xml]
[--echo] [--neighborhood <std::vector<int>>] [--]
[--version] [-h] <std::string> <std::string>
Where:
--returnparameterfile <std::string>
Filename in which to write simple return parameters (int, float,
int-vector, etc.) as opposed to bulk return parameters (image,
geometry, transform, measurement, table).
--processinformationaddress <std::string>
Address of a structure to store process information (progress, abort,
etc.). (default: 0)
--xml
Produce xml description of command line arguments (default: 0)
--echo
Echo the command line arguments (default: 0)
--neighborhood <std::vector<int>>
The size of the neighborhood in each dimension (default: 1,1,1)
--, --ignore_rest
Ignores the rest of the labeled arguments following this flag.
--version
Displays version information and exits.
-h, --help
Displays usage information and exits.
<std::string>
(required) Input volume to be filtered
<std::string>
(required) Output filtered
Description: The MedianImageFilter is commonly used as a robust approach
for noise reduction. This filter is particularly efficient against
'salt-and-pepper' noise. In other words, it is robust to the presence of
gray-level outliers. MedianImageFilter computes the value of each output
pixel as the statistical median of the neighborhood of values around the
corresponding input pixel.
Author(s): Bill Lorensen
Acknowledgements: This command module was derived from
Insight/Examples/Filtering/MedianImageFilter (copyright) Insight
Software Consortium
More Information
Acknowledgment
This work is part of the National Alliance for Medical Image Computing (NAMIC), funded by the National Institutes of Health through the NIH Roadmap for Medical Research, Grant U54 EB005149. Information on the National Centers for Biomedical Computing can be obtained from National Centers for Biomedical Computing.