Difference between revisions of "Documentation/4.1/Developers"
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
* [http://massmail.bwh.harvard.edu/mailman/listinfo/slicer-devel Developers mailing list] / [http://slicer-devel.65872.n3.nabble.com/ Browse archives] | * [http://massmail.bwh.harvard.edu/mailman/listinfo/slicer-devel Developers mailing list] / [http://slicer-devel.65872.n3.nabble.com/ Browse archives] | ||
: Intended for discussion of programming related questions | : Intended for discussion of programming related questions | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
=== Resources === | === Resources === | ||
| Line 63: | Line 60: | ||
* [[Slicer4:QtPort/Releases|Change logs and release details]] | * [[Slicer4:QtPort/Releases|Change logs and release details]] | ||
: Informations about Slicer releases | : Informations about Slicer releases | ||
| + | |||
| + | |bgcolor="#CCCCCC"| | ||
| + | |valign="top"| | ||
=== Step by step - Develop a module or an extension === | === Step by step - Develop a module or an extension === | ||
| Line 106: | Line 106: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | <hr> | ||
[[{{collaborator|logo|slicer4}}|x300px|center]] | [[{{collaborator|logo|slicer4}}|x300px|center]] | ||
Revision as of 06:35, 15 June 2012
Home < Documentation < 4.1 < Developers
3D Slicer is a free open source extensible software application for medical image computing and visualization. Mainly written in C++ and based on the NA-MIC kit, 3D Slicer relies on a variety of libraries: VTK, ITK, CTK, CMake, Qt and Python.
To ensure the stability of the application, relying on a robust software process, the source code is compiled and tested on a daily basis on a variety of platform configurations. The testing results are summarized and reported using a web-based centralized CDash dashboard. Developers of 3D Slicer can also report issues on the open mailing list or using web-based bug tracking system.
3D Slicer consists of both a lean application core and modules offering specific functionality. The core implements the user interface, provides support for data input/output (IO) and visualization and also exposes developer interfaces that support extension of the application with new modules.
Three types of modules are supported: CLI, Loadable module and Scripted module. While the developer has to choose between one of the 3 types to implement its module, the end user won't notice the difference as they all share the same look & feel. The choice for a given type of module is usually based on the type of inputs/parameters for a given module.
These modules can be either built-in or installed on demand via the extensions manager.
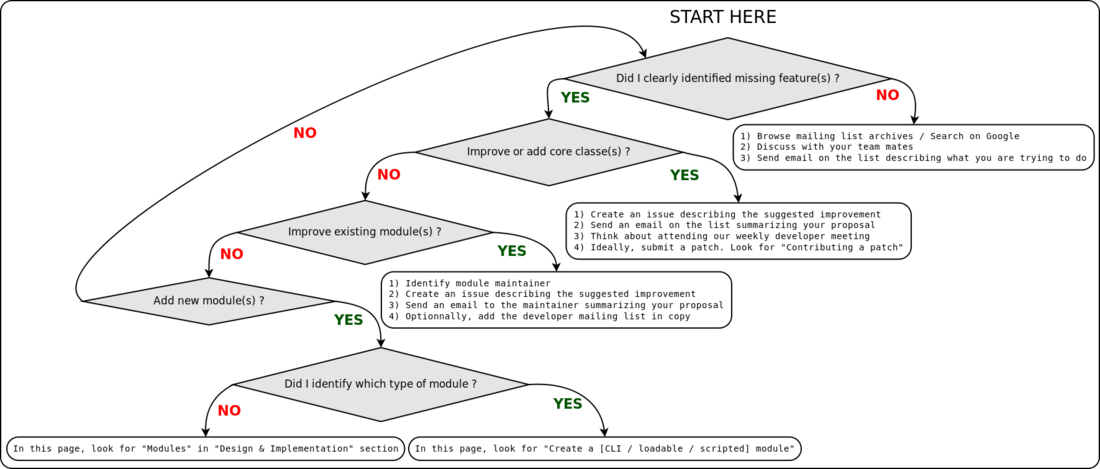
Add or improve a functionality: Where to start ?
Developer references
Getting involved
Resources
|
Step by step - Develop a module or an extensionBuild instructions
Design & Implementation
|
|