Difference between revisions of "Documentation/4.1/Developers/StartHere"
m |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
{{documentation/{{documentation/version}}/Developers/random-image}} | {{documentation/{{documentation/version}}/Developers/random-image}} | ||
| Line 8: | Line 7: | ||
3D Slicer consists of both a lean application core and modules offering specific functionality. The core implements the user interface, provides support for data input/output (IO) and visualization and also exposes developer interfaces that support extension of the application with new modules. | 3D Slicer consists of both a lean application core and modules offering specific functionality. The core implements the user interface, provides support for data input/output (IO) and visualization and also exposes developer interfaces that support extension of the application with new modules. | ||
| − | + | Multiple types of modules are supported: [[Documentation/{{documentation/version}}/Developers/Modules#Command_Line_Interface_.28CLI.29|CLI]], [[Documentation/{{documentation/version}}/Developers/Modules#Loadable_Modules|Loadable module]], [[Documentation/{{documentation/version}}/Developers/Modules#Scripted_Modules|Scripted module]] and [[Documentation/{{documentation/version}}/Developers/EditorExtension|Editor effect]]. While the developer has to choose between one of the 3 types to implement its module, the end user won't notice the difference as they all share the same look & feel. The choice for a given type of module is usually based on the type of inputs/parameters for a given module. | |
These modules can be either built-in or installed on demand via the [[Documentation/{{documentation/version}}/SlicerApplication/ExtensionsManager|extensions manager]]. | These modules can be either built-in or installed on demand via the [[Documentation/{{documentation/version}}/SlicerApplication/ExtensionsManager|extensions manager]]. | ||
Revision as of 18:52, 15 June 2012
Home < Documentation < 4.1 < Developers < StartHere3D Slicer is a free open source extensible software application for medical image computing and visualization. Mainly written in C++ and based on the NA-MIC kit, 3D Slicer relies on a variety of libraries: VTK, ITK, CTK, CMake, Qt and Python.
To ensure the stability of the application, relying on a robust software process, the source code is compiled and tested on a daily basis on a variety of platform configurations. The testing results are summarized and reported using a web-based centralized CDash dashboard. Developers of 3D Slicer can also report issues on the open mailing list or using the web-based bug tracking system.
3D Slicer consists of both a lean application core and modules offering specific functionality. The core implements the user interface, provides support for data input/output (IO) and visualization and also exposes developer interfaces that support extension of the application with new modules.
Multiple types of modules are supported: CLI, Loadable module, Scripted module and Editor effect. While the developer has to choose between one of the 3 types to implement its module, the end user won't notice the difference as they all share the same look & feel. The choice for a given type of module is usually based on the type of inputs/parameters for a given module.
These modules can be either built-in or installed on demand via the extensions manager.
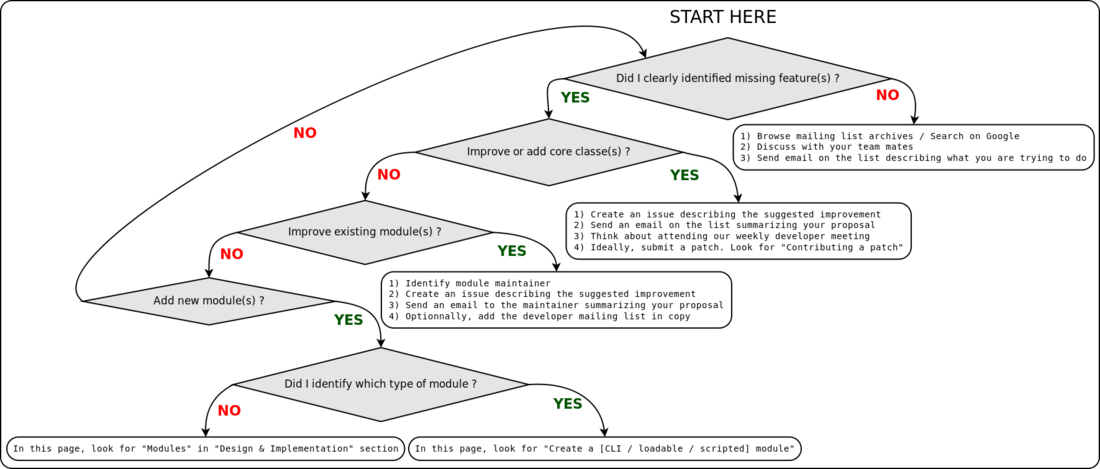
Step by step - Develop a module or an extension
- Where to start?
- Build Slicer application
- Create
- Bundle your module(s) into a Slicer extension
- Build, test, package and distribute extensions