Documentation/4.8/Modules/GeodesicSlicer
|
For the latest Slicer documentation, visit the read-the-docs. |
Introduction and Acknowledgements
|
The module has been developed based on ideas and feedbacks from the community. We would like to especially thank:
- Dr. Olivier Etard, M.D., Ph.D., CHU de Caen.
- Dr. Clément Nathou, M.D., Ph.D., CHU de Caen.
- Dr. Sonia Dollfus, M.D., Ph.D., CHU de Caen, header of ISTS.
- Dr. Csaba Pinter, MSc, Queen's University.
- Dr. Andras Lasso, Ph.D., Queen's University.
If you use this module, please cite the following article: [1].
Contents
Module Description
This module calculates geodesic path in 3D structure. Thanks to this geodesic path, this module can draw an EEG 10-20 system, determine the projected scalp TMS site and correct the rTMS resting motor threshold by correction factor
Terminology
- Mesh A mesh or polygon mesh is a collection of vertices, edges and faces that defines the shape of a polyhedral object in 3D computer graphics and solid modeling.
- Shortest path In graph theory, the shortest path problem is the problem of finding a path between two vertices (or nodes) in a graph such that the sum of the weights of its constituent edges is minimized.
- 10-20 EEG system The International 10-20 system is commonly used for electroencephalogram (EEG) electrode placement and to correlate external skull locations with underlying cortical areas.[2]
Use Cases
The overall goal is to allow users to find the shortest paths between nodes in a graph and via the Dijkstra's algorithm to make 10-20 system. This module can be used for:
- Stimulation in psychiatry
- Surgery measurement
- 3D printing
Panels and their use
Create a mesh
A typical straightforward Geodesic Slicer workflow for consists of the following steps:
- Load a volume.nii.
- Enter in the Geodesic Slicer module using either the toolbar or the Modules menu button.
- Press the button "Create a mesh".
- Wait a moment.
- If the segmentation is fine, press the button "Use this mesh".
- If your image was named 't1.nii' the output will be called 't1.stl', in the same directory of your initial image.
- Go to Parameters to find the shortest path or Make 10-20 EEG system electrode section.
Parameters to find the shortest path
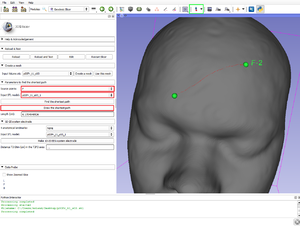
- Source points: The list of fiducial points on the curve, since the "Create-and-place Fiducial" button (in green in the figure above).
- Input STL model: The model you use (after "use this mesh", the t1.stl created).
- Find the shortest path: Calculate in centimeter the geodesic (shortest) path via the Dijkstra's algorithm.
- Draw the shortest path: Draw the Dijkstra's algorithm shortest path.
- Length (cm): The length of the current curve is shown in centimeter.
10-20 system electrode
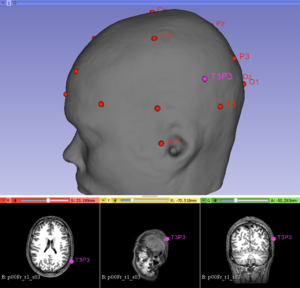
Run the Dijkstra's algorithm to make the 10-20 system electrode distances.
- Source points: The list of fiducial points on the curve, since the "Create-and-place Fiducial" button (in green in the figure above). Four anatomical landmarks are used for the essential positioning of the electrodes (in this order!):
- 1/the nasion
- 2/the inion
- 3/the pre auricular to the left ear
- 4/the pre auricular to the right ear
- Input STL model: The model you use (after "use this mesh", the t1.stl created).
- Press the button "Make 10-20 EEG system electrode" to draw the 10-20 EEG system via the Dijkstra's algorithm.
- The traditional T3P3 site according to the International 10–20 system of electroencephalogram and an anatomical target defined as the best stimulation site to decrease auditory verbal hallucinations and located in the left temporo-parietal cortex [3] was identified.
Information for Developers
The code is available at Github.
References
- ↑ Briend F. et al., Personalized or standardized target for the treatment of auditory hallucinations by rTMS? Biological Psychiatry, submitted
- ↑ Jasper, H.H. The ten-twenty electrode system of the International Federation. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol., 1958, 10: 370-375
- ↑ Hoffman RE. et al., Transcranial magnetic stimulation of Wernicke’s and Right homologous sites to curtail “voices”: a randomized trial. Biol Psychiatry 2013;73:1008–14