Documentation/Nightly/Modules/KSliceInteractiveSegmenter
Introduction and Acknowledgements
|
This work is part of the National Alliance for Medical Image Computing (NA-MIC), funded by the National Institutes of Health through the NIH Roadmap for Medical Research, Grant U54 EB005149. Information on NA-MIC can be obtained from the NA-MIC website. Author: Ivan Kolesov, Georgia Institute of Technology | |||||||
|
Module Description
This is an interactive segmentation approach that is guided by the user throughout the task.
Tutorials
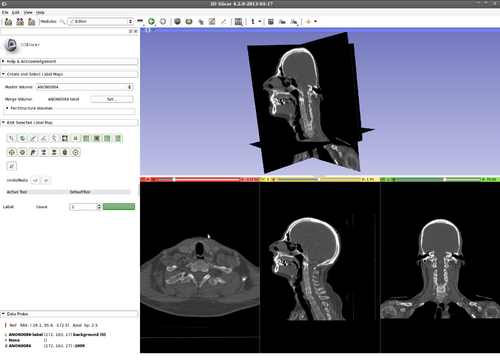
Step 1.) Add data volume to segment
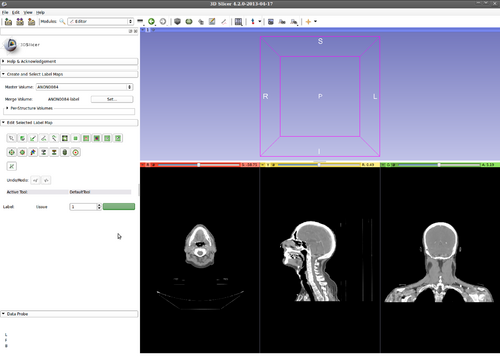
Step 2.) Go to the “Editor” module, select the volume loaded in Step 1 as the “Master Volume” in the “Create and Select Label Maps” drop-down menu
Step 3.) Select the “KSlice” effect in the “Edit Selected Label Map” drop-down menu
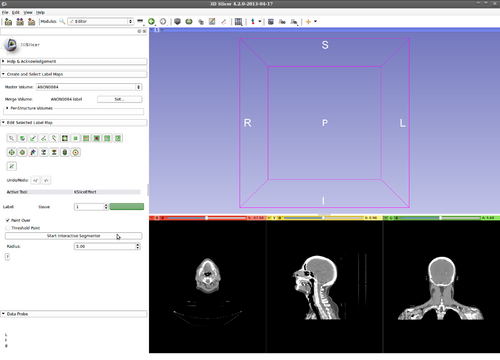
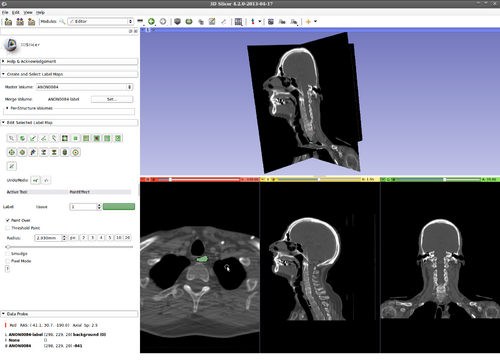
Step 4.) Set the “Radius” parameter and press the “Start Interactive Segmentor” button ( KSlice is now running in the background until the “Stop Interactive Segmentor” button is pressed)
Step 5.) Turn “On” all three slice views in the 3D Plane
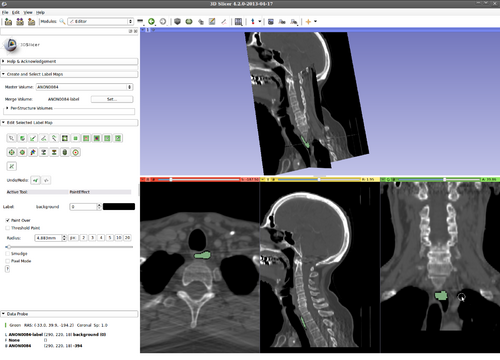
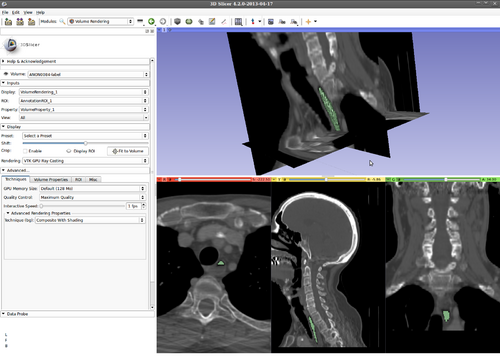
Step 5.) Select the “PaintEffect” tool and initialize KSlice by drawing inside the structure of interest
(green circle, inside the esophagus in this example)
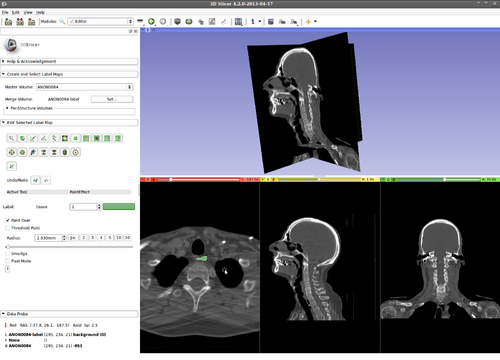
Step 6.) Hover the mouse over a slice view (we focus on the “Red” slice first, here) and press the “Q” key to evolve a 2D active contour in this plane
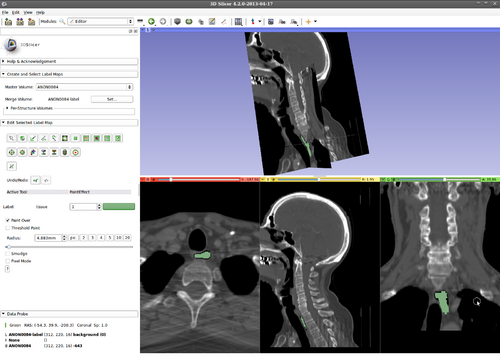
Step 7.) Press the “C” key to copy the current segmentation in this 2D plane, then press the left/right arrow on the keyboard to move on to an adjacent slice, press the “V” key to paste the label, thereby initializing the current slice
Step 8.) Evolve the 2D contour on this slice by pressing “Q”
Step 9.) Hover mouse over the yellow, then green slices and repeat (as many times as desired) Steps 6-8
- As necessary, at any time in the process *****
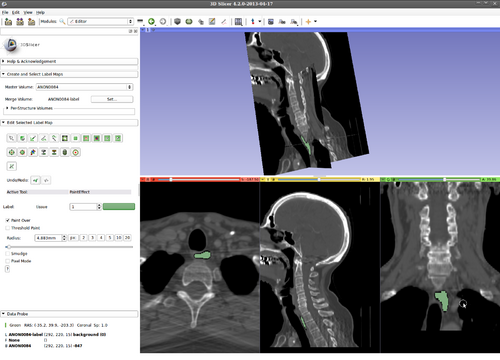
Step 10.) Press the “A” key to change drawing modes (between Draw/Delete label). Thus, if the user's expert knowledge of anatomy does not agree with the current segmentation results, he adds negative input by erasing a label. By deleting in the same area multiple times, the user input is accumulated and this guiding signal forces the changes to become persistent
Step 11.) Alternatively, a user can press “A” again to return to drawing. If a contour is not reaching an area that is, in fact, part of the structure of interest, the user can add positive input by painting this area
Step 12.) Evolve the contour with the changed user input, and new initialization
- Optional visualization ******************
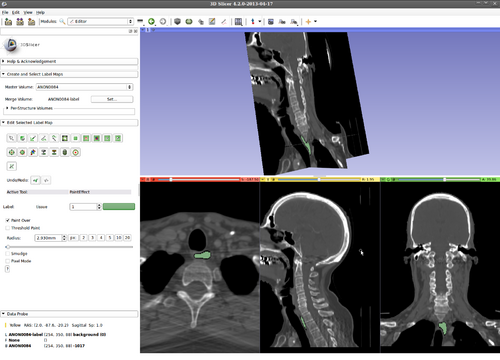
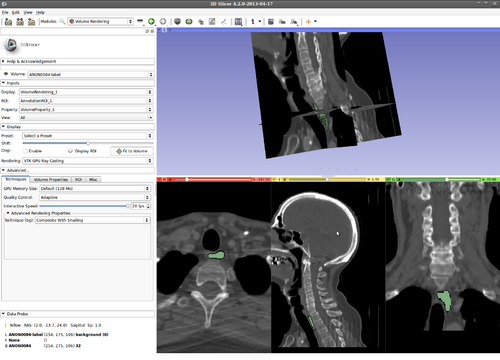
Step 13.) Turn on “Volume Rendering” of the label image in 3D (notice the parameters set for faster interaction). This will be updated during the evolution
Step 14.) Evolution in 3D is done by pressing the “W” key
Panels and their use
N/A
References
- Kolesov, I., Karasev, P., Muller, G., Chudy, K., Xerogeanes, J., and Tannenbaum, A., “Human supervisory control framework for interactive medical image segmentation,” in International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI) Computational Biomechanics for Medicine Workshop, Proceeding of the, 2011.
- Karasev, P., Kolesov, I., Chudy, K., Muller, G., Xerogeanes, J., and Tannenbaum, A., “Interactive mri segmentation with controlled active vision,” in IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Proceedings of the, IEEE, Dec. 2011.
- Karasev, P., Kolesov, I., Fritscher, K., Vela, P., Mitchell, P., and Tannenbaum, A.. “Interactive Medical Image Segmentation using PDE Control Of Active Contours”. In: Medical Imaging, IEEE Transactions on (In Submission) (2013)
- Xerogeanes, J., Mitchell, P. , Karasev, P., Kolesov, I. and Romine, S. . “An Anatomic and Morphologic Evaluation of the Quadriceps Tendon Using 3D MRI Reconstruction: Applications for ACL Autograft Choice and Procurement”. In: Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery (In Submission) (2013)
Information for Developers
| Section under construction. |