Slicer4:Extensions
This page is a place holder right now and will be populated eventually.
Contents
Introduction
- 3D Slicer now supports plug-ins which we call extensions. Extensions are available from an extension server. This allows end-users to select the extensions useful to them, without having to download the entire extension archive.
- The process of creating an extension is as follows:
- create a module (command line, scripted or loadable)
- make sure that it compiles on all supported platforms
- create an s3ext file pointing to the source code
- talk to the slicer team to integrate it into the nightly build process.
- We are using NITRC as the primary repository for contributed extensions, however any subversion or cvs repository can be used. As a general rule, the slicer team does not test the extensions. Use them at your own risk.
- Look at the Associations section of the slicer project page on NITRC for other software that can be used to extend slicer. here to see a listing of Slicer 3 extensions on NITRC.
- Extensions are compiled as part of the nightly build. In order to have your extension compiled nightly and made available to end users, please contact the Slicer team (provide a .s3ext file as described below).
- In order to start your own extension, you can look at the sources for these examples and copy one that looks similar:
http://viewvc.slicer.org/viewcvs.cgi/trunk/Extensions/
- Several example modules are hosted on the nitrc.org site and can be used as a template. These include the major types of loadable and scripted modules.
- Here is a link to user documentation on extensions.
This work was sponsored in part by the collaboration between NA-MIC and NITRC.
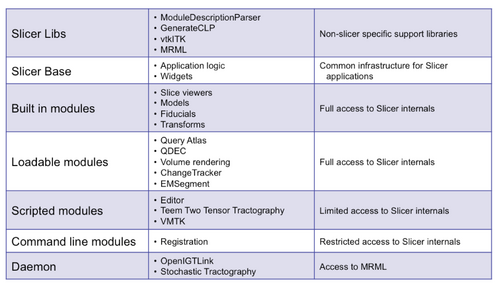
Module Types
The following types of modules are available:
- command line modules - executables that follow the Slicer Execution Model
- scripted modules - Tcl or Python scripts that implement the callbacks of the Module GUI API or the Slicer Execution Model
- loadable modules - shared libraries that implement the Module GUI API and can call/extend the C++ API directly (can provide subclasses of vtk/itk/kwwidgets/MRML/slicer code and other libraries).
All three module types are dynamically discovered by slicer at run time.
See Jim Miller's presentation from the NA-MIC 2010 All Hands Meeting and Steve Pieper's presentation from the 2010 Summer Project Week.
For generic module templates, see the examples on nitrc.org. For a fully fleshed out working example, see the Vascular Modeling Toolkit (vtmk) project which includes a loadable module of vtk/itk code along with several python scripted modules that implement the kwwidgets-based user interface.
Versions
Version 4.0
Documentation Guidelines
This section is intended primarily for the developers. However, improvements from the community are very welcome and encouraged.
Module documentation on the Slicer wiki
- Please copy the template linked below, paste it into your page and customize it with your module's information.
Slicer4:Module_Documentation-4.0_Template
- Please adhere to the naming scheme for the module documentation: [ [Modules:MyModuleNameNoSpaces-Documentation-3.7|My Module Name With Spaces] ] (First Last Name)
- You can use the following python script to automatically generate some of the wiki documentation from your module's .xml file: SEMToMediaWiki.py
Documentation in the module
- Short help file in the help section of the module. Keep in mind that our users are not computer scientists with a background in computer vision.
- Please add a pointer to the documentation on the Slicer wiki to the the Help tab of the module. See the Models module for an example in C++ and Editor module for an example in python.
- Acknowledgements:
- The contributor (and their manager/advisor), the lab (with labs/institution logo) and the funding source (with grant number, logo optional) are listed in the Acknowledegment tab of the module. Please see the Models module for an example. The people listed in the acknowledgement will be the primary people for support and maintenance relative of the module. See here for more information.
- Style Guide: All acknowledgment icons should be 100x100 pixels, preferably in png format.
- Accessing logos: Icons for BIRN, NAC, NA-MIC and IGT are included in
qSlicerLogos.qrcand resources for them are inSlicer4\Resources\Logos. - Adding logos: Please add additional image resources and logo icons to these files as required in order to promote shared use (and to prevent duplication in the code.)