Documentation/4.1/Modules/FacetedVisualizer
Introduction and Acknowledgements
|
Extension: FacetedVisualizer | |||||||
|
Faceted visualizer enables user to create flexible visualizations using Slicer4 by combining 3D digital atlas and 3D scene models with an ontology. This visualizer is primarily intended as a learning tool (e.x. neuroanatomy) and allows users to employ "drill-down" search starting from a specific user typed query by showing the related options extracted by searching the ontology. Currently, the faceted visualizer has been tested with the SPL-PNL Brain atlas and the SPL Abdominal atlas and the FMA ontology. The Radlex ontology is currently not supported by the visualizer.
Module Description
The faceted visualizer integrates an ontology with a 3D Atlas for combined visualization with relevant textual information extracted from the ontology. The visualizer module employs a hierarchical search on the ontology to obtain the visualizations. The visualizer supports simple (e.g. "putamen", "motor system", etc), to complex queries ("liver;arterial supply + stomach + kidney;arterial supply").
Use Cases
Tutorials
Panels and their use
The GUI consists of two main panels. The "User Query" page and "AtlasDBSync" page. The "User Query page" is where the user interacts with the visualizer to produce the visualizations. The "AtlasDBSync" page helps to integrate the ontology with the 3D models contained in the atlas. The visualizer module automatically tries to find appropriate mappings of the 3D models with the ontology. But for models where exact matches aren't found, the visualizer module tries to find all the matching entries from the DB. The interface in the "AtlasDBSync" page allows user to check the mappings found by the module and set up the correct mappings between the ontology and the DB.
User Query Page
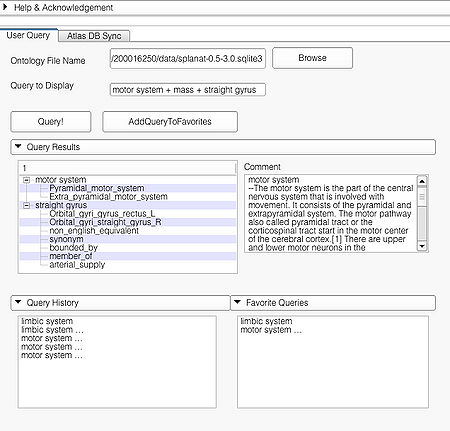
File:APIUserPage.jpg User Page GUI |
This page is useful for creating visualizations based on user typed queries. The user inputs consist of the Ontology File Name and Query To Display. The button Query fires a query and causes the module to start processing the user query for visualization. The button AddQueryToFavorites adds the last typed user query to the list of favorite queries. The favorite query list is shown in the bottom panel Favorite Queries. Additionally, the interface also shows a history of typed queries in the panel Query History.
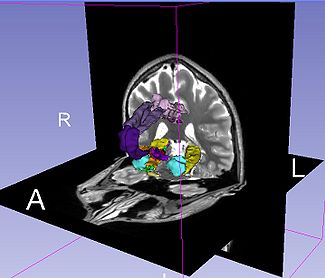
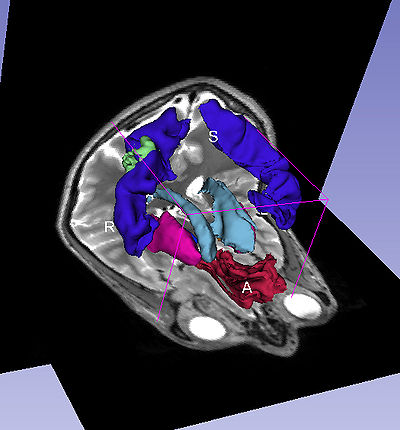
The Query Results panel shows the result of a query, consisting of all the associated predicates and parts for the query. The Figure User Page GUI shows the result of a simple query "limbic system".Additionally, the interface also shows a Comment that contains any relevant textual information about the query obtained from the ontology. The user can refine a search by selecting from the query result. Optionally, the user can also select by clicking on any selection from the Query History or Favorite Queries panel to redo search and visualization. The interface supports the multiple selections to form complex queries. The visualization resulting by searching with the query "Limbic system" is shown below.
Querying Specifics
The faceted visualization module supports the following types of queries:
- Simple Queries e.g. "putamen", "limbic system"
- Complex Queries e.g. "limbic system + mass", and
- Specialized Queries e.g. "liver;arterial_supply"
Simple Queries
Simple query is a self-contained individual string that is matched in entirely with the ontology. An example of a simple query is "limbic system". The result of this query is shown above.
Complex Queries
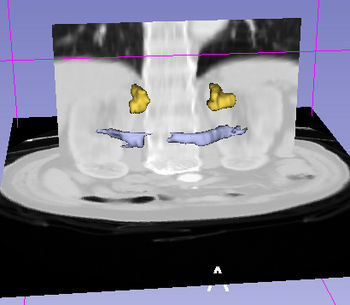
A complex query contains two or more simple or specialized queries. A complex query is typically specified by using a "+". Note that the "+" does not signify an ANDing of the search terms. Instead each string separated by the "+" is searched as an individual query in the ontology. The result of using a complex query is shown below. The Application interface shows the results for all the terms that are matched in the ontology (i.e. the motor system and straight gyrus.) Unmatched terms such as the user added models (e.g. mass) are only displayed. The figure shows an example of a complex query comprised of simple queries.
Specialized Queries
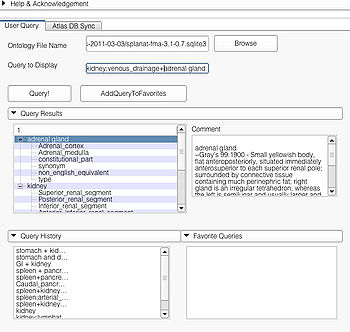
A specialized query helps to search for a query with additional constraints typically using an ANDing operation. Specialized query is specified using a ";" between the search terms. In terms of search in the ontology, the ";" will either result in a search involving the first term as the Subject or Object and the second term as the Predicate(e.g. "straight gyrus;synonym"). In the case where the second term is not a predicate but a part of the preceding term, e.g. "limbic system;Fornix", the visualizer logic automatically detects that the succeeding term is an individual search term and produces the visualization using the succeeding term as the search string resulting in the visualization of query "Fornix".
Specialized queries can be combined with other simple or specialized queries to form complex queries (e.g. "motor system + straight gyrus;synonym"). An example of a complex query using specialized and simple query terms is shown below.
Query Interface
The user can query by typing the query in the Query to Display box or by selecting from one of Query Results, Query History, and Favorite Query panels. All the panels support multiple selection. Multiple selection will result in a complex query. An example of multiple selection from the Query Results panels is shown below. However, it is not possible to create a complex query by selecting from multiple panels (e.g. selecting "some string in Query Results" and "some other string in Query History").
Selecting a string from the Query Result panel will result in creating a specialized query. Example of such a selection is shown below. Multiple selections from the "Query Result" pane will result in a complex query using specialized query terms as shown.
Queries can also be obtained by selecting from the Query History pane and the Favorite Queries pane. Both support multiple selections as shown below.
AtlasDBSync Page
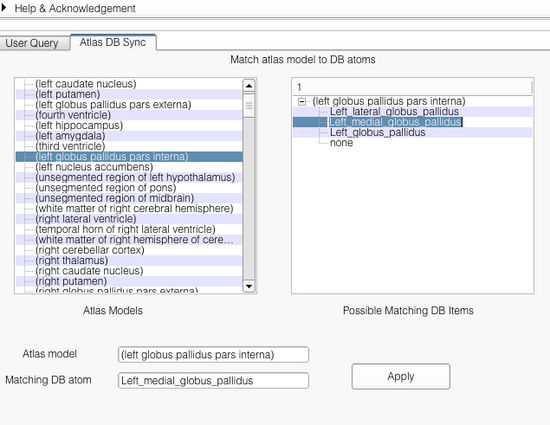
The faceted visualizer module does not require the user to explicitly set the mappings between the the 3D scene atlas and the ontology database before use. Everytime a scene is loaded and an ontology file is set, the module automatically tries to compute matches between the models in the atlas with terms in the ontology. Matching is done in two-passes. In the first pass, the model names (excluding numbers etc) in the atlas are matched exactly (except for white spaces and case) with the terms in the ontology. When a match is found, the mapping between a given model (name) and the database term is stored. For those models where no match is found, a second-pass match is performed. In the second-pass, a relaxed matching is performed where substrings of the model name string is matched with the terms in the ontology. This step usually creates non-unique matches. As a result, the mappings are not set automatically. Instead the matching options from the ontology are stored and can be selected by the user. The user can accomplish this from the "AtlasDBSync" page.
Application interface
The application interface is shown below. As shown, the interface shows the list of all the models found in the atlas. Selecting an atlas model on the left pane shows the corresponding matches found in the right pane. The user can set the match by selecting appropriate matching string from the right pane. Upon selection from the right pane, both the atlas model and the selected ontology term are shown in the bottom Atlas model and Matching DB atom. The user can confirm the match by clicking on the button Apply.
Similar Modules
References
- Xiaodong Tao, Ming-ching Chang, “A Skull Stripping Method Using Deformable Surface and Tissue Classification”, SPIE Medical Imaging, San Diego, CA, 2010.
- Ming-ching Chang, Xiaodong Tao “Subvoxel Segmentation and Representation of Brain Cortex Using Fuzzy Clustering and Gradient Vector Diffusion”, SPIE Medical Imaging, San Diego, CA, 2010.
Information for Developers
| Section under construction. |