Documentation/Nightly/Modules/EpileptogenicFocusDetection
|
For the latest Slicer documentation, visit the read-the-docs. |
Introduction and Acknowledgements
|
This work was supported by Comision Sectorial de Investigacion Cientıfica (CSIC, Universidad de la Republica, Uruguay) under program "Proyecto de Inclusión Social". |
Module Description
In refractory epilepsy, the goal of neuroimaging is to localize the region of seizure onset. Tracers that accumulate and remain fixed proportional to regional cerebral blood flow (rCBF) at the time of injection are used to obtain SPECT images of the brain activity during and between seizures. This module was developed to detect epileptogenic focus candidates using basal and ictal SPECT images. A MRI image can also be used. Below you will find how to detect epileptogenic focus candidates using this module.
Use Cases
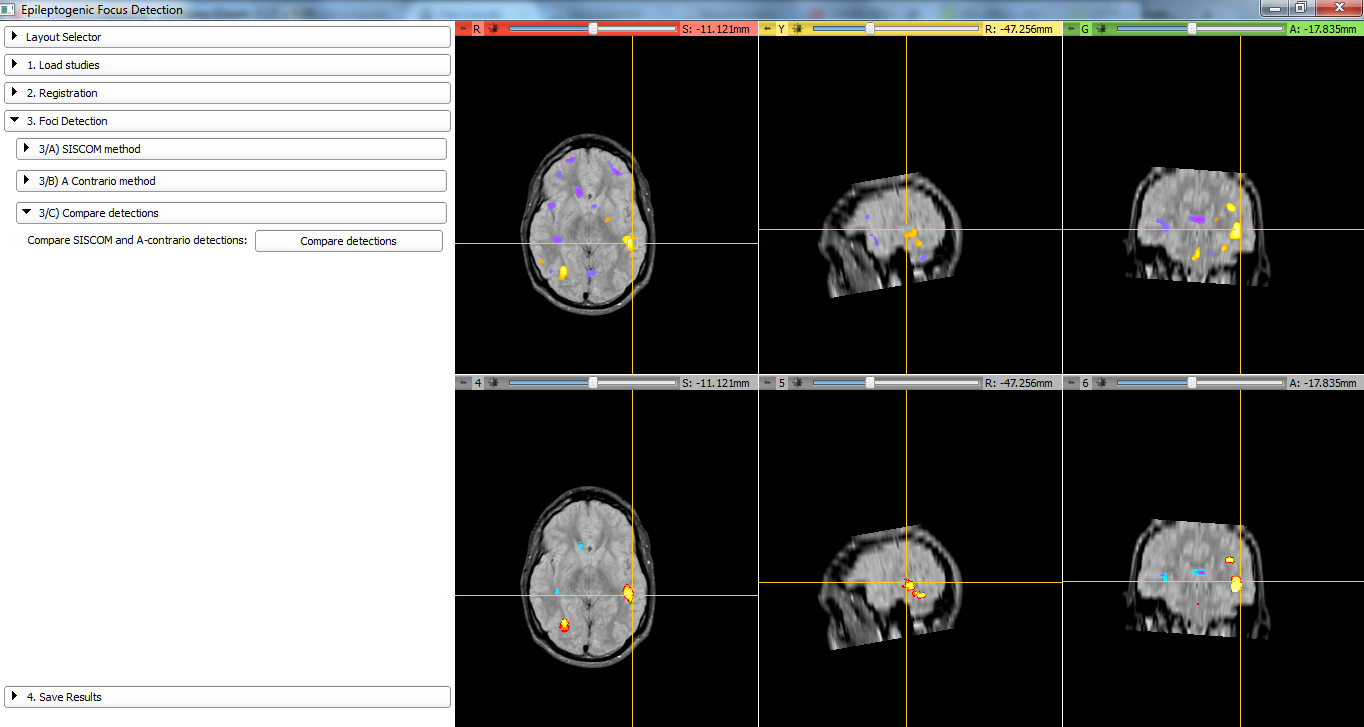
Compare candidates obtained using SISCOM and a-contrario method.
Tutorials
N/A
Panels and their use
- Load Studies: The following studies are required:
- SPECT basal
- SPECT ictal
- MRI (optional: for visualization of the results or SPECT/MRI registration)
- Registration: To compare the basal SPECT and the icatl SPECT the volumes must be registered. In this step it is possible to perform:
- SPECT basal/SPECT ictal registration
- SPECT/MRI registration (if MRI Available)
- SPECT basal/SPECT ictal mask (intersection) computation
- Foci detection: Differential (SISCOM) and a-contrario methods are implemented. Results can be visualized in MRI Space (if available) or SPECT Space. Results can be compared.
- Differential method: The most used technique for detecting the epileptogenic zone(EZ) is to threshold the co-registered and normalized subtraction of these two images. This method has proven to be very useful but has the disadvantage that the result depends on the selected threshold.
- A-contrario: to be described
Similar Modules
N/A
References
N/A
Information for Developers
| Section under construction. |