Difference between revisions of "Documentation/Nightly/Modules/AADDiffusionWeightedData"
From Slicer Wiki
Acsenrafilho (talk | contribs) m |
Acsenrafilho (talk | contribs) m |
||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
{{documentation/{{documentation/version}}/module-section|Module Description}} | {{documentation/{{documentation/version}}/module-section|Module Description}} | ||
| − | This module offers a simple application of the AAD filter on diffusion-weighted imaging data. Since the noise through the image space is present in the tensorial acquisition, the AAD filter could be applied in order to decrease the noise amplitude and maintain the geometrical details of the image. | + | This module offers a simple application of the [[Documentation/Nightly/Modules/AADImageFilter|AAD filter]] on diffusion-weighted imaging data. Since the noise through the image space is present in the tensorial acquisition, the AAD filter could be applied in order to decrease the noise amplitude and maintain the geometrical details of the image. |
<!-- ---------------------------- --> | <!-- ---------------------------- --> | ||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
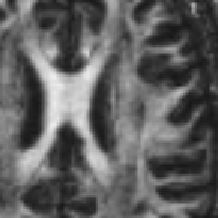
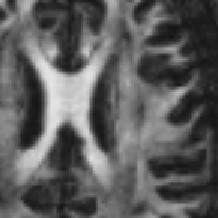
** The raw DWI data could be filtered using the AAD approach, which was previously applied on structural MRI data<ref>Da S Senra Filho, A. C., Garrido Salmon, C. E., & Murta Junior, L. O. (2015). Anomalous diffusion process applied to magnetic resonance image enhancement. Physics in Medicine and Biology, 60(6), 2355–2373. doi:10.1088/0031-9155/60/6/2355</ref> and Diffusion Tensor Imaging images as well<ref> doi:</ref> | ** The raw DWI data could be filtered using the AAD approach, which was previously applied on structural MRI data<ref>Da S Senra Filho, A. C., Garrido Salmon, C. E., & Murta Junior, L. O. (2015). Anomalous diffusion process applied to magnetic resonance image enhancement. Physics in Medicine and Biology, 60(6), 2355–2373. doi:10.1088/0031-9155/60/6/2355</ref> and Diffusion Tensor Imaging images as well<ref> doi:</ref> | ||
| − | <gallery widths="300px" perrow=" | + | <gallery widths="300px" heights="300px" perrow="2"> |
| − | Image: | + | Image:DTI_FA_raw.png|Raw DTI FA map |
| − | Image: | + | Image:DTI_FA_AAD.png|DTI FA map filtered with AAD filter (q=1.2) |
| + | Image:Tractography_AAD.png|Tractography example using filtered FA map | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| Line 45: | Line 46: | ||
IO: | IO: | ||
*Input Volume | *Input Volume | ||
| − | **Select the input image | + | **Select the DWI input image |
*Output Volume | *Output Volume | ||
| − | **Set the output image file which the filters should place the final result | + | **Set the output DWI image file which the filters should place the final result |
Diffusion Parameters: | Diffusion Parameters: | ||
*Conductance | *Conductance | ||
| − | **The conductance regulates the diffusion intensity in the neighbourhood area. Choose a higher conductance if the input image has strong noise seem in the whole image space. | + | **A float value for edge preservation adjustment. The conductance regulates the diffusion intensity in the neighbourhood area. Choose a higher conductance if the input image has strong noise seem in the whole image space. If you want an automatic evaluation to conductance variable, please select the following methods |
| + | *Use Auto Conductance | ||
| + | **Choose if you want to use an automatic adjustment of conductance parameter. If this is checked, the inserted value is ignored and the optimization function below is used. | ||
| + | *Optmization Function | ||
| + | **A set of optimization function for automatic estimation of conductance parameter. This is helpful is you do not have an initial guess on what value is appropriate to the conductance setting. (Canny, MAD and Morphological). Please see the [http://www.insight-journal.org/browse/publication/983 Insight-Journal article] that explain each of these automatic conductance adjusment methods. | ||
*Number of Iteractions | *Number of Iteractions | ||
| + | **A integer value that defines the number of iterations. | ||
| + | *Time Step | ||
| + | **A double value that regulates the numerical stability of the algorithm. It is safe to maintain the upper limit with the formulation given by Anisotropic Diffusion algorithm (See GradientAnisotropiDiffusionImageFilter in ITK documentation). | ||
| + | *Anomalous Parameter | ||
| + | **A double value that defines the q-Gaussian probability distribution function which is convoluated in each neighborhood in the image. | ||
<!-- ---------------------------- --> | <!-- ---------------------------- --> | ||
{{documentation/{{documentation/version}}/module-section|Similar Modules}} | {{documentation/{{documentation/version}}/module-section|Similar Modules}} | ||
Revision as of 16:21, 19 July 2017
Home < Documentation < Nightly < Modules < AADDiffusionWeightedData
|
For the latest Slicer documentation, visit the read-the-docs. |
Introduction and Acknowledgements
|
Extension: AnomalousFilters | |||||||
|
Module Description
This module offers a simple application of the AAD filter on diffusion-weighted imaging data. Since the noise through the image space is present in the tensorial acquisition, the AAD filter could be applied in order to decrease the noise amplitude and maintain the geometrical details of the image.
Use Cases
- Use Case 1: Decrease noise in DWI data
Tutorials
N/A
Panels and their use
IO:
- Input Volume
- Select the DWI input image
- Output Volume
- Set the output DWI image file which the filters should place the final result
Diffusion Parameters:
- Conductance
- A float value for edge preservation adjustment. The conductance regulates the diffusion intensity in the neighbourhood area. Choose a higher conductance if the input image has strong noise seem in the whole image space. If you want an automatic evaluation to conductance variable, please select the following methods
- Use Auto Conductance
- Choose if you want to use an automatic adjustment of conductance parameter. If this is checked, the inserted value is ignored and the optimization function below is used.
- Optmization Function
- A set of optimization function for automatic estimation of conductance parameter. This is helpful is you do not have an initial guess on what value is appropriate to the conductance setting. (Canny, MAD and Morphological). Please see the Insight-Journal article that explain each of these automatic conductance adjusment methods.
- Number of Iteractions
- A integer value that defines the number of iterations.
- Time Step
- A double value that regulates the numerical stability of the algorithm. It is safe to maintain the upper limit with the formulation given by Anisotropic Diffusion algorithm (See GradientAnisotropiDiffusionImageFilter in ITK documentation).
- Anomalous Parameter
- A double value that defines the q-Gaussian probability distribution function which is convoluated in each neighborhood in the image.
Similar Modules
References
- da S Senra Filho, A.C., Garrido Salmon, C.E. & Murta Junior, L.O., 2015. Anomalous diffusion process applied to magnetic resonance image enhancement. Physics in Medicine and Biology, 60(6), pp.2355–2373. DOI: 10.1088/0031-9155/60/6/2355
Information for Developers
| Section under construction. |