Difference between revisions of "Documentation/Nightly/Modules/CropVolume"
(Prepend documentation/versioncheck template. See http://na-mic.org/Mantis/view.php?id=2887) |
|||
| Line 64: | Line 64: | ||
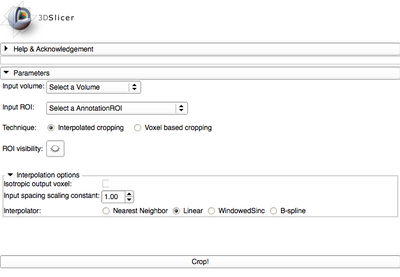
*** '''Isotropic output voxel''' if this checkbox is selected, the output image will have isotropic spacing, with the voxel size of the output image in each dimension equal to the ''smallest'' voxel dimension of the input image multiplied by the scaling constant. | *** '''Isotropic output voxel''' if this checkbox is selected, the output image will have isotropic spacing, with the voxel size of the output image in each dimension equal to the ''smallest'' voxel dimension of the input image multiplied by the scaling constant. | ||
*** '''Input spacing scaling constant''' is the coefficient used to determine the spacing of the output volume. The output spacing is defined by multiplying the input spacing in each dimension by the user-specified coefficient. For example, if the input spacing is 1x1x1.4, and the scaling coefficient is 0.5, the output volume will have spacing 0.5x0.5x0.7, effectively doubling the resolution of the output image. | *** '''Input spacing scaling constant''' is the coefficient used to determine the spacing of the output volume. The output spacing is defined by multiplying the input spacing in each dimension by the user-specified coefficient. For example, if the input spacing is 1x1x1.4, and the scaling coefficient is 0.5, the output volume will have spacing 0.5x0.5x0.7, effectively doubling the resolution of the output image. | ||
| − | *** '''Interpolator''' allows to select between Nearest Neighbor, Linear, Windowed Sinc or B-spline interpolators (see [[Documentation/ | + | *** '''Interpolator''' allows to select between Nearest Neighbor, Linear, Windowed Sinc or B-spline interpolators (see [[Documentation/Nightly/Modules/ResampleScalarVectorDWIVolume | Resample Scalar/Vector/DWI Volume]] for details). For subvolumes being extracted from a label volume, you should use Nearest Neighbor interpolator. Otherwise B-spline is the preferred choice. Linear interpolator requires less computation, which may be important for very large ROIs. |
** '''Crop!''' button initiates the subvolume extraction based on the inputs and parameters. | ** '''Crop!''' button initiates the subvolume extraction based on the inputs and parameters. | ||
| Line 70: | Line 70: | ||
{| | {| | ||
| − | |[[Image: | + | |[[Image:CropVolume-4.3-GUI-panel.png|thumb|400px|CropVolume control panel]] |
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 16:28, 7 November 2013
Home < Documentation < Nightly < Modules < CropVolume
|
For the latest Slicer documentation, visit the read-the-docs. |
Introduction and Acknowledgements
|
This work is part of the National Alliance for Medical Image Computing (NA-MIC), funded by the National Institutes of Health through the NIH Roadmap for Medical Research, Grant U54 EB005149. Information on NA-MIC can be obtained from the NA-MIC website. The development of this module was supported in part by NIH CA111288 and CA151261. | |||||||
|
Module Description
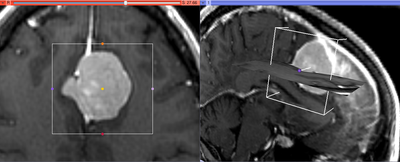
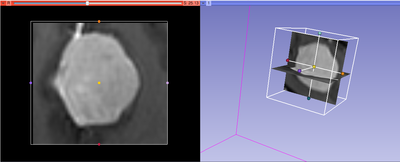
This module allows to extract rectangular subvolume from a scalar image, with the subvolume defined by Slicer ROI widget.
You can use this module to crop a DTI or DWI volume.
The cropping functionality of this module is enabled by Resample Scalar/Vector/DWI Volume module, which is called internally.
Use Cases
|
Most frequently used for these scenarios:
|
|
Tutorials
Not available at this time, but see the list of Slicer 3.6 tutorials that use CropVolume here: Modules:CropVolume-Documentation-3.6.
Panels and their use
|
|
Cropping of oblique sub-volumes can be done by placing either or both of input volume and ROI under transform(s). These transforms will be taken into account while preparing the output.
Similar Modules
References
N/A
Information for Developers
| Section under construction. |