Difference between revisions of "Announcements:Slicer3.4"
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
The community of Slicer developers is proud to announce the release of Slicer 3.4. | The community of Slicer developers is proud to announce the release of Slicer 3.4. | ||
| − | + | Click here to [http://www.slicer.org/pages/Downloads download] different versions of Slicer3 and find pointers to the source code, mailing lists and bug tracker. Please note that Slicer continues to be a research package and is not intended for clinical use. Testing of functionality is an ongoing activity with high priority, however, some features of Slicer3 are not fully tested. | |
| − | <gallery widths=" | + | |
| − | Image:Slicer3.4.png | + | |
| − | Image: | + | ==Highlights== |
| + | <gallery caption="Slicer v3.4 - New and Improved Feature Highlights" widths="250px" heights="150px" perrow="4"> | ||
| + | Image:analysis_result.jpg|[[Modules:ChangeTracker-Documentation-3.4 |'''Change Tracker''']] is a software tool for quantification of the subtle changes in pathology. | ||
| + | Image:Femesh-in-trunk-120808.png|[[Modules:IA_FEMesh-Documentation-3.4 |'''IA-FEMesh Module''']]: A loadable module to automate the creation of surface and volumetric meshes for finite element analysis. | ||
| + | Image:Tracts_glyphs_90degrees.jpg|The [[Modules:Volumes:Diffusion_Editor-Documentation-3.4|'''Diffusion Editor''']] is a 3D Slicer module, which allows modifying parameters (gradients, bValues, measurement frame) of DWI data and provides a quick way to interpret them. | ||
| + | Image:FiducialGlyphs.jpg|The [[Modules:Fiducials-Documentation-3.4 |'''Fiducials Module''']] creates and manages lists of Fiducial points. | ||
| + | Image:Volren.png|[[Modules:VolumeRendering-Documentation-3.4 |'''Volume Rendering''']] allows the rendering of volumes in 3D view in semi transparent mode, potentially combined with the models in one scene. | ||
| + | Image:FetchMIDoc SlicerInformatics1.png|[[Modules:FetchMI-Documentation-3.4|'''FetchMI''']] (Fetch Medical Informatics) is a 'sandbox' functionality being developed to remotely upload, download and tag Slicer scenes and datasets. | ||
| + | Image:QAsearch.png|The [[Modules:QueryAtlas-Documentation-3.4 |'''Query Atlas''']] is a 3D Slicer module that allows the use of atlas-based anatomical representations, linked to underlying semantic descriptions, as an interactive 3D spatial reference for viewing experimental results and for performing information searches to study and interpret them. | ||
| + | Image:B-spline-reg.png|The [[Documentation-3.4#Registration |'''Register Images Module''']] is an integrated framework providing access to ITK registration technologies. Algorithms can be run in single mode or pipelined. | ||
| + | Image:LinearRegistration.png|The [[Modules:LinearRegistration-Documentation-3.4| '''Linear Registration''']] command line module implements a registration algorithm based on the Mattes mutual information registration metric. This module is often used to align images of the same subject acquired at different times. | ||
| + | Image:EMSegment-Workflow.png|The [[Modules:EMSegment-TemplateBuilder |'''EMSegment Template Builder Module''']] is the primary Slicer3 interface to the EMSegment algorithm (Pohl et al.), an automatic segmentation algorithm for medical images. | ||
| + | Image:Roi tract.jpg|[[Modules:ROISeeding-Documentation-3.4 |'''ROI Seeding''']] is a tractography implementation that allows a user to seed tracts from a region of interest (ROI). The ROI is defined as a labelmap and has to be provided by the user. | ||
| + | Image:FiducialSeeding.png| The [[Modules:FiducialSeeding-Documentation-3.4 |'''Fiducial Seeding Module''']] is used for interactive seeding of DTI fiber tracts starting from a list of fiducials or vertices of a model. | ||
| + | Image:DTIDisplayGlyphs.png|The [[Modules:DTIDisplay-Documentation-3.4 |'''Fiber Bundles Module''']] is used for loading, saving, and changing the appearance of DTI fiber tracts. | ||
| + | Image:SlicesModule.png|The [[Modules:Slices-Documentation-3.4 |'''Slices Module''']] provides access to all Slice nodes in a single panel. | ||
| + | Image:SlicerColorDisplayWidget-3.4.jpg|The [[Modules:Color-Documentation-3.4 |'''Color Module''']] manages color look up tables. Look-up Tables (LUTs) are used by mappers to translate between an integer and a color value for display of models and volumes. | ||
| + | Image:EditorModule.png|The [[Modules:Editor-Documentation-3.4 |'''Interactive Editor''']] is a set of tools to create label maps to identify structures volumes. | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
==New Features in Slicer 3.4== | ==New Features in Slicer 3.4== | ||
Slicer 3.4 has many new features! Please also note that many of these new features are still being developed and will be improved in future releases, so you may encounter some unexpected behavior. If you do encounter unexpected behavior, you can join the Slicer users' mailing by sending email to [mailto:slicer-users-request@massmail.spl.harvard.edu?subject=subscribe slicer-users-request@massmail.spl.harvard.edu] with the subject "subscribe", and report the behavior there to see if there is a work around (or check the [http://massmail.spl.harvard.edu/pipermail/slicer-users/ archives]), and to the [http://www.na-mic.org/Bug bug tracker] if it needs to be solved by the developers. | Slicer 3.4 has many new features! Please also note that many of these new features are still being developed and will be improved in future releases, so you may encounter some unexpected behavior. If you do encounter unexpected behavior, you can join the Slicer users' mailing by sending email to [mailto:slicer-users-request@massmail.spl.harvard.edu?subject=subscribe slicer-users-request@massmail.spl.harvard.edu] with the subject "subscribe", and report the behavior there to see if there is a work around (or check the [http://massmail.spl.harvard.edu/pipermail/slicer-users/ archives]), and to the [http://www.na-mic.org/Bug bug tracker] if it needs to be solved by the developers. | ||
| − | |||
===New Features=== | ===New Features=== | ||
| Line 39: | Line 57: | ||
==[[Documentation-3.4|Pages with reference manual style documentation of the modules in Slicer 3.4]]== | ==[[Documentation-3.4|Pages with reference manual style documentation of the modules in Slicer 3.4]]== | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Reporting Bugs== | ==Reporting Bugs== | ||
| Line 72: | Line 72: | ||
== Acknowledgments == | == Acknowledgments == | ||
| − | [http://www.slicer.org/slicerWiki/index.php/Announcments-3. | + | [http://www.slicer.org/slicerWiki/index.php/Announcments-3.4-Team The Slicer Development Team] |
This work is part of the National Alliance for Medical Image Computing (NAMIC), funded by the National Institutes of Health through the NIH Roadmap for Medical Research, Grant U54 EB005149. Information on the National Centers for Biomedical Computing can be obtained from http://nihroadmap.nih.gov/bioinformatics. This work was also supported by NIH grant P41 RR13218 ([http://spl.harvard.edu/nac NAC]) and the [http://www.nbirn.net Biomedical Informatics Research Network]. | This work is part of the National Alliance for Medical Image Computing (NAMIC), funded by the National Institutes of Health through the NIH Roadmap for Medical Research, Grant U54 EB005149. Information on the National Centers for Biomedical Computing can be obtained from http://nihroadmap.nih.gov/bioinformatics. This work was also supported by NIH grant P41 RR13218 ([http://spl.harvard.edu/nac NAC]) and the [http://www.nbirn.net Biomedical Informatics Research Network]. | ||
Revision as of 20:38, 26 May 2009
Home < Announcements:Slicer3.4Introduction
The community of Slicer developers is proud to announce the release of Slicer 3.4.
Click here to download different versions of Slicer3 and find pointers to the source code, mailing lists and bug tracker. Please note that Slicer continues to be a research package and is not intended for clinical use. Testing of functionality is an ongoing activity with high priority, however, some features of Slicer3 are not fully tested.
Highlights
- Slicer v3.4 - New and Improved Feature Highlights
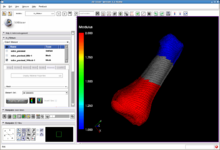
Change Tracker is a software tool for quantification of the subtle changes in pathology.
IA-FEMesh Module: A loadable module to automate the creation of surface and volumetric meshes for finite element analysis.
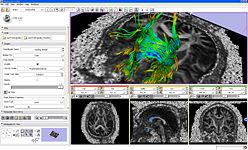
The Diffusion Editor is a 3D Slicer module, which allows modifying parameters (gradients, bValues, measurement frame) of DWI data and provides a quick way to interpret them.
The Fiducials Module creates and manages lists of Fiducial points.
Volume Rendering allows the rendering of volumes in 3D view in semi transparent mode, potentially combined with the models in one scene.
FetchMI (Fetch Medical Informatics) is a 'sandbox' functionality being developed to remotely upload, download and tag Slicer scenes and datasets.
The Query Atlas is a 3D Slicer module that allows the use of atlas-based anatomical representations, linked to underlying semantic descriptions, as an interactive 3D spatial reference for viewing experimental results and for performing information searches to study and interpret them.
The Register Images Module is an integrated framework providing access to ITK registration technologies. Algorithms can be run in single mode or pipelined.
The Linear Registration command line module implements a registration algorithm based on the Mattes mutual information registration metric. This module is often used to align images of the same subject acquired at different times.
The EMSegment Template Builder Module is the primary Slicer3 interface to the EMSegment algorithm (Pohl et al.), an automatic segmentation algorithm for medical images.
ROI Seeding is a tractography implementation that allows a user to seed tracts from a region of interest (ROI). The ROI is defined as a labelmap and has to be provided by the user.
The Fiducial Seeding Module is used for interactive seeding of DTI fiber tracts starting from a list of fiducials or vertices of a model.
The Fiber Bundles Module is used for loading, saving, and changing the appearance of DTI fiber tracts.
The Slices Module provides access to all Slice nodes in a single panel.
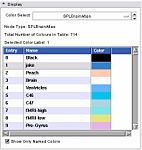
The Color Module manages color look up tables. Look-up Tables (LUTs) are used by mappers to translate between an integer and a color value for display of models and volumes.
The Interactive Editor is a set of tools to create label maps to identify structures volumes.
New Features in Slicer 3.4
Slicer 3.4 has many new features! Please also note that many of these new features are still being developed and will be improved in future releases, so you may encounter some unexpected behavior. If you do encounter unexpected behavior, you can join the Slicer users' mailing by sending email to slicer-users-request@massmail.spl.harvard.edu with the subject "subscribe", and report the behavior there to see if there is a work around (or check the archives), and to the bug tracker if it needs to be solved by the developers.
New Features
- Welcome Module at Startup
- Improved Save Module
- Improved Editor
- New Registration module
- New Slices module
- Fiducial based tractography
- Improved SceneSnapshot Screen Capture functionality
- Compare View and Cross Hairs
- Support for Extension Server for installing plug-ins
- Improved Dicom Support
- MRML scenes and all data load from and save into XNAT desktop
Links to the Latest Slicer 3.4 Binaries
Including:
- 64-bit Linux
- 32-bit Linux
- Darwin PPC
- Darwin x86
- Windows
Pages with reference manual style documentation of the modules in Slicer 3.4
Reporting Bugs
Please go to http://www.na-mic.org/Bug/ and report bugs for Slicer version 3.
Where to go for Help
Compilation/development questions can be sent to the Slicer Developers Mailing List. Questions about running Slicer can be sent to the Slicer Users Mailing List.
Subscription management tools and archives are available at:
http://massmail.bwh.harvard.edu/mailman/listinfo/slicer-devel
http://massmail.bwh.harvard.edu/mailman/listinfo/slicer-users
Acknowledgments
This work is part of the National Alliance for Medical Image Computing (NAMIC), funded by the National Institutes of Health through the NIH Roadmap for Medical Research, Grant U54 EB005149. Information on the National Centers for Biomedical Computing can be obtained from http://nihroadmap.nih.gov/bioinformatics. This work was also supported by NIH grant P41 RR13218 (NAC) and the Biomedical Informatics Research Network.