Difference between revisions of "Modules:StochasticTractography-Documentation-3.4"
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
===Module Description=== | ===Module Description=== | ||
| − | As a main purpose, the stochastic tractography module helps to evaluate connectivity in the White Matter between two regions of the Grey Matter of the brain | + | As a main purpose, the stochastic tractography module helps to evaluate connectivity in the White Matter between two regions of interest (ROIs) of the Grey Matter of the brain. These ROIs define grey matter regions ensuring a specific neurophysiological function. Extensively, study involving more than two regions could still be done by pairing the regions two by two and computing them separetely to finally gather the results. |
== Usage == | == Usage == | ||
| − | * want to study fiber | + | * You want to study fiber path from a single region of interest (ROI) |
| − | * want to evaluate connectivity between two ROIs | + | * You want to evaluate connectivity between two ROIs |
Revision as of 19:55, 15 April 2009
Home < Modules:StochasticTractography-Documentation-3.4Return to Slicer 3.4 Documentation
Module Name
Stochastic Tractography
General Information
Module Type & Category
Type: Interactive
Category: DTI
Authors, Collaborators & Contact
- Author: Julien von Siebenthal
- Contributor: Steve Pieper
- Contact: jvs@bwh.harvard.edu
Module Description
As a main purpose, the stochastic tractography module helps to evaluate connectivity in the White Matter between two regions of interest (ROIs) of the Grey Matter of the brain. These ROIs define grey matter regions ensuring a specific neurophysiological function. Extensively, study involving more than two regions could still be done by pairing the regions two by two and computing them separetely to finally gather the results.
Usage
- You want to study fiber path from a single region of interest (ROI)
- You want to evaluate connectivity between two ROIs
Description
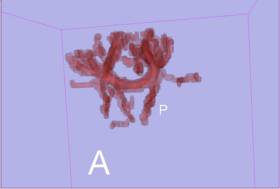
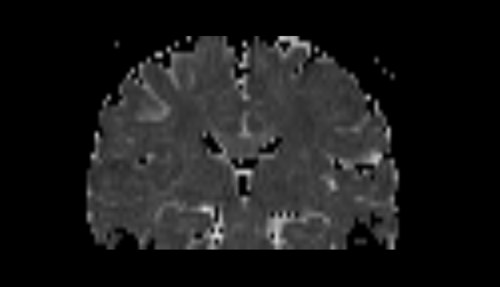
With the stochastic tractography module, you can:
|
|
|
|
|
|
Quick Tour of Features and Use
List all the panels in your interface, their features, what they mean, and how to use them. For instance:
- IO panel:
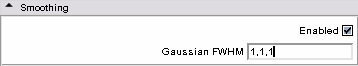
- Smoothing panel:
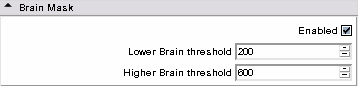
- Brain Mask panel:
- Diffusion Tensor panel:
- Tractography panel:
- Connectivity Map panel:
Development
Dependencies
Volumes
Known bugs
Follow this link to the Slicer3 bug tracker.
Usability issues
Follow this link to the Slicer3 bug tracker. Please select the usability issue category when browsing or contributing.
Source code & documentation
More Information
Acknowledgment
National Alliance for Medical Image Computing (NAMIC), funded by the National Institutes of Health through the NIH Roadmap for Medical Research, Grant U54 EB005149 (to Ron Kikinis, Marek Kubicki).
References
- Björnemo M, Brun A, Kikinis R, Westin CF. Regularized stochastic white matter tractography using diffusion tensor MRI. In Fifth International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI'02). Tokyo, Japan, 2002;435-442.
- Friman, O., Farneback, G., Westin CF. A Bayesian Approach for Stochastic White Matter Tractography. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, Vol 25, No. 8, Aug. 2006
- Shenton, M.E., Ngo, T., Rosenberger, G., Westin, C.F., Levitt, J.J., McCarley, R.W., Kubicki, M. Study of Thalamo-Cortical White Matter Fiber Tract Projections in Schizophrenia Using Diffusion Stochastic Tractography. Poster presented at the 46th Meeting of the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology, Boca Raton, FL, December 2007.