Difference between revisions of "Documentation/Nightly/Extensions/ScatteredTransform"
Grandwork2 (talk | contribs) |
Grandwork2 (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
The resulting B-Spline transform can be used to warp 3D images, a process which is very time consuming if spatial interpolation is performed using the mesh [1]. | The resulting B-Spline transform can be used to warp 3D images, a process which is very time consuming if spatial interpolation is performed using the mesh [1]. | ||
{| | {| | ||
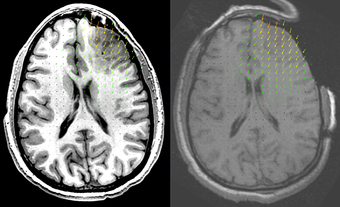
| − | |[[Image: | + | |[[Image:ScatteredTransform_displacementField.png|thumb|340px|Brain shift computed using a biomechanics model and FEM. The deformed high resolution pre-operative image (left) is compared to the intra-operative image (right). The pre-operative image has been warped using the B-Spline obtained by applying ScatteredTransform to the original and deformed mesh nodal positions.]] |
|[[Image:SkullStripperOutput-3-6.png|thumb|340px|Brain mask as contour]] | |[[Image:SkullStripperOutput-3-6.png|thumb|340px|Brain mask as contour]] | ||
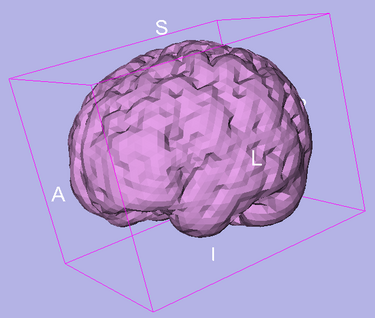
|[[Image:SkullStripperSurface-3-6.png|thumb|375px|Brain surface]] | |[[Image:SkullStripperSurface-3-6.png|thumb|375px|Brain surface]] | ||
Revision as of 04:40, 3 March 2017
Home < Documentation < Nightly < Extensions < ScatteredTransform
|
For the latest Slicer documentation, visit the read-the-docs. |
Introduction and Acknowledgements
|
Extension: ScatteredTransform |
Module Description
Creates a BSpline transform from a displacement field defined at scattered points by using the Multi-level BSpline interpolation algorithm.
Use Cases
1. Create a B-Spline transform based on two sets of fiducials.
2. Create a B-Spline transform based on two sets of points read from files. These files can contain the initial and deform configurations for a biomechanics-based FEM or mesh-free registration. The resulting B-Spline transform can be used to warp 3D images, a process which is very time consuming if spatial interpolation is performed using the mesh [1].
Panels and their use
References
1. Joldes GR, Wittek A, Warfield SK, Miller K (2012) "Performing Brain Image Warping Using the Deformation Field Predicted by a Biomechanical Model." In: Nielsen PMF, Miller K, Wittek A, editors. Computational Biomechanics for Medicine: Deformation and Flow: Springer New York. pp. 89-96.