|
|
| Line 71: |
Line 71: |
| | | | |
| | {| | | {| |
| − | |[[Image:Slicer4_ExtractSubvolumeROI_controls.jpg|thumb|250px|CropVolume control panel]] | + | |[[Image:Slicer4_ExtractSubvolumeROI_controls.jpg|thumb|500px|CropVolume control panel]] |
| | | | |
| | |} | | |} |
Revision as of 03:15, 21 November 2011
Home < Documentation < 4.0 < Modules < CropVolume
Introduction and Acknowledgements
|
This work is part of the National Alliance for Medical Image Computing (NA-MIC), funded by the National Institutes of Health through the NIH Roadmap for Medical Research, Grant U54 EB005149. Information on NA-MIC can be obtained from the NA-MIC website. The development of this module was supported in part by NIH CA111288 and CA151261.
Author: Andrey Fedorov, Ron Kikinis, SPL
Contact: Andrey Fedorov, <email>fedorov@bwh.harvard.edu</email>
|
|
|
Module Description
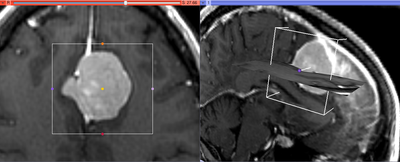
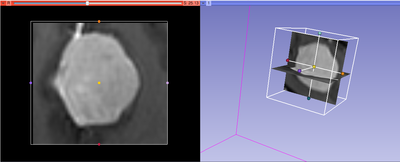
This module allows to extract rectangular subvolume from a scalar image, with the subvolume defined by Slicer ROI widget.
You can use this module to crop a DTI or DWI volume.
Use Cases
|
Most frequently used for these scenarios:
- You are trying to segment an object that occupies small portion of the image. Cropping the ROI with that object can simplify your segmentation task and reduce both the memory requirements and processing time.
- You are trying to register two objects that occupy smaller portions of the image. In this scenario, cropping will allow you to focus the processing at the region of interest, and simplify registration initialization.
|
|
Tutorials
Not available at this time, but see the list of Slicer 3.6 tutorials that use CropVolume here: Modules:CropVolume-Documentation-3.6.
Panels and their use
- Input/initialization parameters panel:
- Input volume defines the input image from which you need to crop a subvolume
- ROI is a Region of Interest (see the ROI module documentation), which can be defined outside CropVolume, or by creating new MRMLROINode from the selector menu. The ROI can be adjusted using the widget handles in 3D view panel.
- ROI visibility allows to turn the visibility of the 3D widget on or off in the 3D view panel.
- Output volume is the volume node where the result of ROI extraction will be stored. Note, that the output volume cannot be identical to the input volume. The module will give you an error if this is the case.
- Input spacing scaling constant is the coefficient used to determine the spacing of the output volume. The output spacing is defined by multiplying the input spacing in each dimension by the user-specified coefficient. For example, if the input spacing is 1x1x1.4, and the scaling coefficient is 0.5, the output volume will have spacing 0.5x0.5x0.7, effectively doubling the resolution of the output image.
- Isotropic voxel size if this checkbox is selected, the output image will have isotropic spacing, with the voxel size of the output image in each dimension equal to the smallest voxel dimension of the input image multiplied by the scaling constant.
- Interpolation type allows to select between Nearest Neighbor, Linear or Cubic interpolators. For subvolumes being extracted from a label volume, you should use Nearest Neighbor interpolator. Otherwise Cubic is the preferred choice. Linear interpolator requires less computation, which may be important for very large ROIs.
- Do ROI resample initiates the subvolume extraction based on the inputs and parameters.
- Viewing panel: Size and location of the ROI can be modified using one of the two methods. First, this can be done in 3D View by moving the colored handles of the ROI widget. Second, the ROI can be adjusted in the slice views. Right mouse button click adjusts the bounds of the ROI. Left mouse button click moves the center of ROI to be the point where the click was made.
|
|
Similar Modules
- Point to other modules that have similar functionality
References
Publications related to this module go here. Links to pdfs would be useful.
For extensions: link to the source code repository and additional documentation
Information for Developers
 The section above is generated using the following wiki code:
The section above is generated using the following wiki code:
{{documentation/{{documentation/version}}/module-section|Information for Developers}}
{{documentation/{{documentation/version}}/module-developerinfo|ModuleTemplate|type=Interactive|category=Example}}
If you are documenting a CLI, the category should be extracted from the corresponding XML description. This could be done automatically using the following wiki template:
{{documentation/{{documentation/version}}/module-category|xmlurl=http://path/to/YOURMODULENAME.xml }}
If your module is available in Slicer repository, the following template could be useful to obtain the corresponding URL:
{{documentation/{{documentation/version}}/module-cli-xmlurl|{{documentation/modulename}}|SVNREVISION}}
Using this later template, the final syntax would be:
{{documentation/{{documentation/version}}/module-category|xmlurl={{documentation/{{documentation/version}}/module-cli-xmlurl|{{documentation/modulename}}|SVNREVISION}} }}
![]() The section above is generated using the following wiki code:
The section above is generated using the following wiki code: