Difference between revisions of "Modules:Colors-Documentation-3.6"
| Line 210: | Line 210: | ||
A wiki page on [[Slicer3:LUTs_and_Ontologies | LUTs and Ontologies]] where you can generate a Slicer Color file from a wiki page table. | A wiki page on [[Slicer3:LUTs_and_Ontologies | LUTs and Ontologies]] where you can generate a Slicer Color file from a wiki page table. | ||
| + | |||
| + | To install a new defaul color file, commit it to the source code repository in Base/Logic/Resources/ColorFiles. The Slicer3/Base/Logic/CMakeLists.txt will automatically detect and install all *.txt files to the appropriate binary directory. | ||
===Dependencies=== | ===Dependencies=== | ||
Revision as of 14:22, 7 June 2010
Home < Modules:Colors-Documentation-3.6Return to Slicer 3.6 Documentation
Color Module
Color
General Information
Module Type & Category
Type: Interactive
Category: Base
Authors, Collaborators & Contact
- Nicole Aucoin: Brigham and Women's Hospital
- Sebastien Barre, Kitware Inc.
- Contact: Nicole Aucoin, nicole@bwh.harvard.edu
Module Description
The Color Module manages color look up tables.
Look-up Tables (LUTs) are used by mappers to translate between an integer and a color value for display of models and volumes.
Usage
Use Cases, Examples
This module is especially appropriate for these use cases:
- Use Case 1: change the color mapping of volumes
- In the Volumes module, Display tab, you can select a new color table for grey scale or label map volumes.
- Use Case 2: change model scalar overlays
- In the Models module, Display tab, you can select a new color table to map scalar overlays associated with the model.
- Use Case 3: create new color tables
- Either copy an existing color node or create a new one in the Colors module, Edit tab.
- You can then save it with the scene so it gets loaded again whenever that scene is opened. or copy it into a special directory where it will be loaded whenever Slicer is run.
Examples of the module in use:
- Create a custom color file for a brain segmentation
Tutorials
Links to tutorials explaining how to use this module:
- The Slicer3 Visualization Tutorial uses the Colors module.
Quick Tour of Features and Use
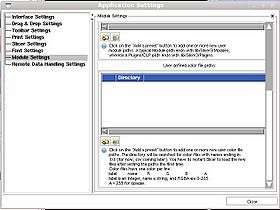
You can specify a directory from which to read color files using the View -> Application Settings window, Module Settings frame. Click on the Add a preset button to add one or more new user color file paths. The directory will be searched for color files with names ending in .txt or .ctbl and loaded on start up. You have to restart Slicer to load the new files after setting the paths the first time.
You can deactivate paths or delete them as well using this interface.
Color files have one color per line:
label name R G B A
label is an integer, name a string, and there are four integers for RGBA in the inclusive range 0-255. The A stands for opacity, use 255 for opaque.
In a the binary directory of Slicer3, the default color files live in share/Slicer3/SlicerBaseLogic/Resources/ColorFiles. In the source directory, they live in Base/Logic/Resources/ColorFiles.
Display panel
This is a stand alone widget that can be popped up by other modules, for example the Editor. Here it lets you inspect the values of the selected colour look up table.
Slicer supports three kinds of tables:
- Continuous scales, like the greyscale table.
- Parametric tables, defined by an equation, such as the FMRIPA table.
- Discrete tables, such as those read in from a file.
- Color Select: Choose from a drop down list of color nodes.
The colors are divided up into categories. These descriptions can be found in the Help and Acknowlegements tab at the top of the module's GUI.
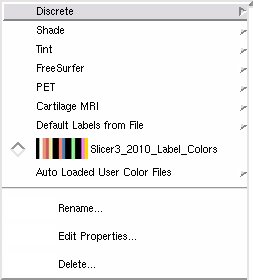
- Discrete
 Labels: A legacy colour table that contains some anatomical mapping
Labels: A legacy colour table that contains some anatomical mapping FullRainbow: A full rainbow of 256 colors, goes from red to red with all rainbow colors in between. Useful for colourful display of a label map
FullRainbow: A full rainbow of 256 colors, goes from red to red with all rainbow colors in between. Useful for colourful display of a label map Grey: A grey scale ranging from black at 0 to white at 255. Useful for displaying MRI volumes.
Grey: A grey scale ranging from black at 0 to white at 255. Useful for displaying MRI volumes. Iron: A scale from red to yellow, 157 colours, useful for
Iron: A scale from red to yellow, 157 colours, useful for Rainbow: Goes from red to purple, passing through the colors of the rainbow in between. Useful for a colorful display of a label map
Rainbow: Goes from red to purple, passing through the colors of the rainbow in between. Useful for a colorful display of a label map Ocean: A lighter blue scale of 256 values, useful for showing registration results.
Ocean: A lighter blue scale of 256 values, useful for showing registration results. Desert: Red to yellow/orange scale, 256 colours, useful for
Desert: Red to yellow/orange scale, 256 colours, useful for InvertedGrey: A white to black scale, 256 colours, useful to highlight negative versions, or to flip intensities of signal values.
InvertedGrey: A white to black scale, 256 colours, useful to highlight negative versions, or to flip intensities of signal values. ReverseRainbow: A colourful display option, 256 colours going from purple to red
ReverseRainbow: A colourful display option, 256 colours going from purple to red fMRI: A combination of Ocean (0-22) and Desert (23-42), useful for displaying functional MRI volumes (highlights activation)
fMRI: A combination of Ocean (0-22) and Desert (23-42), useful for displaying functional MRI volumes (highlights activation) fMRIPA: A small fMRI positive activation scale going from red to yellow from 0-19, useful for displaying functional MRI volumes when don't need the blue of the fMRI scale.
fMRIPA: A small fMRI positive activation scale going from red to yellow from 0-19, useful for displaying functional MRI volumes when don't need the blue of the fMRI scale. Random: A random selection of 256 rgb colours, useful to distinguish between a small number of labeled regions (especially outside of the brain)
Random: A random selection of 256 rgb colours, useful to distinguish between a small number of labeled regions (especially outside of the brain)- UserDefined: A user defined colour table, use the editor to specify it
 Red: A red scale of 256 values. Useful for layering with Cyan
Red: A red scale of 256 values. Useful for layering with Cyan Green: A green scale of 256 values, useful for layering with Magenta
Green: A green scale of 256 values, useful for layering with Magenta Blue: A blue scale of 256 values from black to pure blue, useful for layering with Yellow
Blue: A blue scale of 256 values from black to pure blue, useful for layering with Yellow Yellow: A yellow scale of 256 values, from black to pure yellow, useful for layering with blue (it's complementary, layering yields gray)
Yellow: A yellow scale of 256 values, from black to pure yellow, useful for layering with blue (it's complementary, layering yields gray) Cyan: A cyan ramp of 256 values, from black to cyan, complementary ramp to red, layering yeilds gray
Cyan: A cyan ramp of 256 values, from black to cyan, complementary ramp to red, layering yeilds gray Magenta: A magenta scale of 256 colors from black to magenta, complementary ramp to green, layering yeilds gray
Magenta: A magenta scale of 256 colors from black to magenta, complementary ramp to green, layering yeilds gray Warm1: A scale from yellow to red, of 256 colors, ramp of warm colours that's complementary to Cool1
Warm1: A scale from yellow to red, of 256 colors, ramp of warm colours that's complementary to Cool1 Warm2: A scale from green to yellow, 256 colours, ramp of warm colours that's complementary to Cool2
Warm2: A scale from green to yellow, 256 colours, ramp of warm colours that's complementary to Cool2 Warm3: A scale from cyan to green, 256 colours, ramp of warm colours that's complementary to Cool3
Warm3: A scale from cyan to green, 256 colours, ramp of warm colours that's complementary to Cool3 Cool1: A scale from blue to cyan, 256 colours, ramp of cool colours that's complementary to Warm1
Cool1: A scale from blue to cyan, 256 colours, ramp of cool colours that's complementary to Warm1 Cool2: A scale from magenta to blue, 256 colours, ramp of cool colours that's complementary to Warm2
Cool2: A scale from magenta to blue, 256 colours, ramp of cool colours that's complementary to Warm2 Cool3: A scale from red to magenta, ramp of cool colours that's complementary to Warm3
Cool3: A scale from red to magenta, ramp of cool colours that's complementary to Warm3 RandomIntegers: A random scale
RandomIntegers: A random scale
- Shade:
 WarmShade1: A scale from black to red, of 256 colors, ramp of warm colors with variation in value that's complementary to CoolShade1
WarmShade1: A scale from black to red, of 256 colors, ramp of warm colors with variation in value that's complementary to CoolShade1 WarmShade2: A scale from black to yellow, through green, of 256 colors, ramp of warm colors with variation in value that's complementary to CoolShade2
WarmShade2: A scale from black to yellow, through green, of 256 colors, ramp of warm colors with variation in value that's complementary to CoolShade2 WarmShade3: A scale from black to green, of 256 colours, ramp of warm colors with variation in value that's complementary to CoolShade3
WarmShade3: A scale from black to green, of 256 colours, ramp of warm colors with variation in value that's complementary to CoolShade3 CoolShade1: A scale from black to cyan, 256 colours, ramp of cool colours with variation in value that is complementary to WarmShade1
CoolShade1: A scale from black to cyan, 256 colours, ramp of cool colours with variation in value that is complementary to WarmShade1 CoolShade2: A scale from black to blue through purple, 256 colors, ramp of cool colours with variation in value that is complementary to WarmShade2
CoolShade2: A scale from black to blue through purple, 256 colors, ramp of cool colours with variation in value that is complementary to WarmShade2 CoolShade3: A scale from black to magenta, 256 colours, ramp of cool colours with variation in value that is complementary to WarmShade3
CoolShade3: A scale from black to magenta, 256 colours, ramp of cool colours with variation in value that is complementary to WarmShade3
- Tint:
 WarmTint1: A scale from white to red, 256 colours, ramp of warm colours with variation in saturation that's complementary to CoolTint1
WarmTint1: A scale from white to red, 256 colours, ramp of warm colours with variation in saturation that's complementary to CoolTint1 WarmTint2: A scale from white to yellow, 256 colours, ramp of warm colours with variation in saturation that's complementary to CoolTint2
WarmTint2: A scale from white to yellow, 256 colours, ramp of warm colours with variation in saturation that's complementary to CoolTint2 WarmTint3: A scale from white to green, 256 colours, ramp of warm colours with variation in saturation that's complementary to CoolTint3
WarmTint3: A scale from white to green, 256 colours, ramp of warm colours with variation in saturation that's complementary to CoolTint3 CoolTint1: A scale from white to cyan, 256 colours, ramp of cool colours with variations in saturation that's complementary to WarmTint1
CoolTint1: A scale from white to cyan, 256 colours, ramp of cool colours with variations in saturation that's complementary to WarmTint1 CoolTint2: A scale from white to blue, 256 colours, ramp of cool colours with variations in saturation that's complementary to WarmTint2
CoolTint2: A scale from white to blue, 256 colours, ramp of cool colours with variations in saturation that's complementary to WarmTint2 CoolTint3: A scale from white to magenta, 256 colours, ramp of cool colours with variations in saturation that's complementary to WarmTint3
CoolTint3: A scale from white to magenta, 256 colours, ramp of cool colours with variations in saturation that's complementary to WarmTint3
- FreeSurfer
 Heat: The Heat FreeSurfer colour table, shows hot spots with high activation
Heat: The Heat FreeSurfer colour table, shows hot spots with high activation BlueRed: A FreeSurfer color scale, 256 colours, from blue to red
BlueRed: A FreeSurfer color scale, 256 colours, from blue to red RedBlue: A FreeSurfer color scale, 256 colours, from red to blue
RedBlue: A FreeSurfer color scale, 256 colours, from red to blue RedGreen: A FreeSurfer color scale, 256 colours, from red to green, used to highlight sulcal curvature
RedGreen: A FreeSurfer color scale, 256 colours, from red to green, used to highlight sulcal curvature GreenRed: A FreeSurfer color scale, 256 colours, from green to red, used to highlight sulcal curvature
GreenRed: A FreeSurfer color scale, 256 colours, from green to red, used to highlight sulcal curvature- FreeSurferLabels: A color table read in from a text file, each line of the format: IntegerLabel Name R G B Alpha
- PET
- Cartilage MRI
- Default Labels from File:
- a list of color nodes loaded from files, from the default Slicer color directory
 PelvisColor: useful for displaying segmented pelvic MRI volumes
PelvisColor: useful for displaying segmented pelvic MRI volumes 64Color-Nonsemantic: A color table with no semantic labels, pure color information
64Color-Nonsemantic: A color table with no semantic labels, pure color information- AbdomenColors: useful for displaying segmented abdominal MRI volumes
- SPL-BrainAtlas-ColorFile: useful for displaying segmented brain MRI volumes
- SPL-BrainAtlas-2009-ColorFile: an updated brain segmentation node
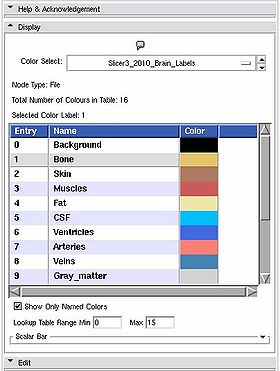
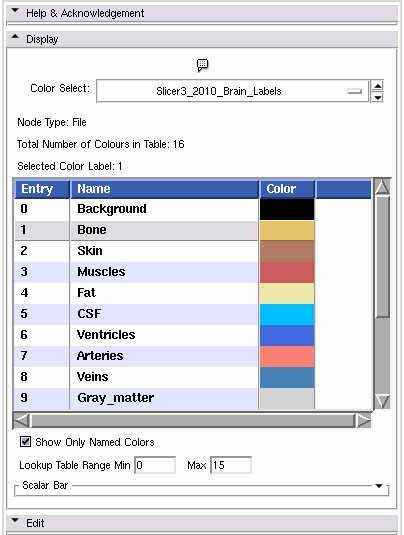
 Slicer3_2010_LabelColors: a table with 16 labels defined.
Slicer3_2010_LabelColors: a table with 16 labels defined.
 Slicer3_2010_Brain_Labels: a brain segementation table with 16 labels defined.
Slicer3_2010_Brain_Labels: a brain segementation table with 16 labels defined.- Auto Loaded User Color Files:
- Files loaded from the user specified color paths in the Module Settings, can be saved with the scene
- File
- If you load a color file from File -> Add Data, it will appear here
- User Generated
- If you create a new color node in the Editor panel, it will appear here
- Node Type: a label updated to give the type of the node currently being displayed
- Total Number of Colours in Table: a label updated to display the number of entries in the color look up table.
- Selected Color Label: used especially in the Editor module, draw with the colour last clicked upon in the table.
- List box: The contents of the colour table, the entry is the integer label value, the name will show up in the label map layer of th 22d slice windows when you mouse over voxels with the corresponding value, the Color column shows how the voxel will be rendered.
- Show Only Named Colors: when this box is checked, the list box will only be populated by named colours. Some colour tables can have memtpy entries that have no name and default to black, this option lets you hide or show them.
- Lookup Table Range Min Max': Changes the range of values displayed, doesn't change the number of values in the table.
Scalar Bar
This panel lets you add a scalar bar widget to the 3D view showing the mapping between the integers and the colors in the color node.
- Display Scalar Bar: click on this to add a scalar bar to the scene, showing the currently selected color node in the Color Select drop down menu
- Title: set the title of the scalar bar, mm is used by default
- Title Properties: set the text display properties of the title text
- Color
- Font
- Style
- Opacity
- Label Format: The label format entry box uses the standard C++ string format. Format documentation
- Label Text Properties: Define how the labels are displayed along the length of the scalar bar widget.
- Color
- Font
- Style
- Opacity
- Maximum number of Colors: set the maximum number of scalar bar segments to show
- Number of labels: set the number of labels to show.
Edit panel
This panel lets users create a new colour look up table file, or edit an existing one.
Use the Edit frame to create a new color table, and save it to the mrml scene.
To create a new color node:
First, give your new color table a name in the Name entry.
Then fill in the Number of Colors. The list box will be populated with the corresponding number of entries. You can reset this to a larger number w/o losing your current settings. Set it to 0 to clear out the list box.
Then click on Generate to populate a new node from the GUI contents. The color node is now available to use in the Volumes or Edit or Save modules. If you've set up user defined color file paths, the node will be set up automatically to save in the first of them.
To edit an existing color node, click on Select a Color Table to Copy. Pick a node from the drop down list, then click on the Copy Node button, it will fill in the edit box with those values. Make any changes you want, then click on the Generate a New Color Node button. At that point, the new node will show up in the File -> Save Data widget.
Development
Notes from the Developer(s)
A wiki page on LUTs and Ontologies where you can generate a Slicer Color file from a wiki page table.
To install a new defaul color file, commit it to the source code repository in Base/Logic/Resources/ColorFiles. The Slicer3/Base/Logic/CMakeLists.txt will automatically detect and install all *.txt files to the appropriate binary directory.
Dependencies
The Volumes, Editor, and Models modules require this module.
Tests
On the Dashboard, these tests verify that the module is working on various platforms:
- vtkMRMLColorNodeTest1 vtkMRMLColorNodeTest1
- vtkMRMLColorTableNodeTest1 vtkMRMLColorTableNodeTest1
- vtkMRMLColorTableStorageNodeTest1 vtkMRMLColorTableStorageNodeTest1
- vtkMRMLdGEMRICProceduralColorNodeTest1 vtkMRMLdGEMRICProceduralColorNodeTest1
- vtkMRMLFreeSurferProceduralColorNodeTest1 vtkMRMLFreeSurferProceduralColorNodeTest1
- vtkMRMLPETProceduralColorNodeTest1 vtkMRMLPETProceduralColorNodeTest1
- vtkMRMLProceduralColorNodeTest1 vtkMRMLProceduralColorNodeTest1
- Slicer3ColorStorageNodeSceneTest Libs/MRML/Testing/Tcl/TestColorStorageNodeInScene.tcl
Known bugs
Follow this link to the Slicer3 bug tracker.
Usability issues
Follow this link to the Slicer3 bug tracker. Please select the usability issue category when browsing or contributing.
Source code & documentation
Source code:
- vtkSlicerColorGUI.cxx
- vtkSlicerColorGUI.h
- vtkSlicerColorLogic.cxx
- vtkSlicerColorLogic.h
- vtkSlicerColorDisplayWidget.cxx
- vtkSlicerColorDisplayWidget.h
- vtkSlicerColorEditWidget.cxx
- vtkSlicerColorEditWidget.h
- vtkMRMLColorNode.cxx
- vtkMRMLColorNode.h
Documentation generated by doxygen.
- Color GUI
- Color Logic
- Color Display Widget
- Color Edit Widget
- MRML Color Node (superclass from which other color nodes are derived)
More Information
Acknowledgment
This work is part of the National Alliance for Medical Image Computing (NAMIC), funded by the National Institutes of Health through the NIH Roadmap for Medical Research, Grant U54 EB005149.