Difference between revisions of "Modules:OrientImages-Documentation-3.6"
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
===Examples, Use Cases & Tutorials=== | ===Examples, Use Cases & Tutorials=== | ||
| − | * This module is useful for transforming volume from its original orientation to a given orientation. | + | * This module is useful for transforming volume from its original orientation to a given orientation. Note, that the module does not align the voxel space axes with the physical space axes. If your input image is not axis-aligned, the output will preserve the direction cosines of the input image. It does not change the spatial position and orientation of the volume in the physical space. |
When combined with "Create a Dicom Series" module, one can synthesize a sagittal acquisition from an axially acquired volume. | When combined with "Create a Dicom Series" module, one can synthesize a sagittal acquisition from an axially acquired volume. | ||
Revision as of 01:26, 27 April 2010
Home < Modules:OrientImages-Documentation-3.6Return to Slicer 3.6 Documentation
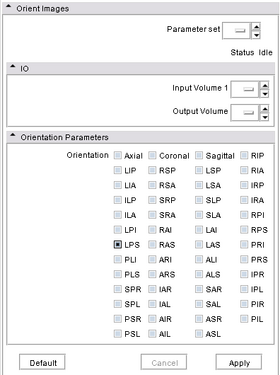
Module Name
Orient Images
General Information
Module Type & Category
Type: CLI
Category: Converters
Authors, Collaborators & Contact
- Author: Bill Lorensen
- Contact: bill.lorensen at gmail.com
Module Description
Orients an output volume. Rearranges the slices in a volume according to the selected orientation. The slices are not interpolated. They are just reordered and/or permuted. The resulting volume will cover the original volume. NOTE: since Slicer3 takes into account the orientation of a volume, the re-oriented volume will not show any difference from the original volume, To see the difference, save the volume and display it with a system that either ignores the orientation of the image (e.g. Paraview) or displays individual images.
Usage
Examples, Use Cases & Tutorials
- This module is useful for transforming volume from its original orientation to a given orientation. Note, that the module does not align the voxel space axes with the physical space axes. If your input image is not axis-aligned, the output will preserve the direction cosines of the input image. It does not change the spatial position and orientation of the volume in the physical space.
When combined with "Create a Dicom Series" module, one can synthesize a sagittal acquisition from an axially acquired volume.
- A command line example of the module is
OrientImage
--orientation Axial
${MRML_DATA}/fixed.nrrd
${TEMP}/OrientImageTestAxial.nrrd
Quick Tour of Features and Use
List all the panels in your interface, their features, what they mean, and how to use them. For instance:
- Input/output panel:
- Parameters panel:
- Viewing panel:
Note, that the module does not align the voxel space axes with the physical space axes. If your input image is not axis-aligned, the output will preserve the direction cosines of the input image.
Development
Dependencies
Other modules or packages that are required for this module's use.
Known bugs
Follow this link to the Slicer3 bug tracker.
Usability issues
Follow this link to the Slicer3 bug tracker. Please select the usability issue category when browsing or contributing.
Source code & documentation
Source Code: OrientImage.cxx
XML Description: Orient orientImage.xml
Usage:
./OrientImage [--processinformationaddress <std::string>] [--xml]
[--echo] [-o <Axial|Coronal|Sagittal|RIP|LIP|RSP|LSP|RIA
|LIA|RSA|LSA|IRP|ILP|SRP|SLP|IRA|ILA|SRA|SLA|RPI|LPI|RAI
|LAI|RPS|LPS|RAS|LAS|PRI|PLI|ARI|ALI|PRS|PLS|ARS|ALS|IPR
|SPR|IAR|SAR|IPL|SPL|IAL|SAL|PIR|PSR|AIR|ASR|PIL|PSL|AIL
|ASL>] [--] [--version] [-h] <std::string> <std::string>
Where:
--processinformationaddress <std::string>
Address of a structure to store process information (progress, abort,
etc.). (default: 0)
--xml
Produce xml description of command line arguments (default: 0)
--echo
Echo the command line arguments (default: 0)
-o <Axial|Coronal|Sagittal|RIP|LIP|RSP|LSP|RIA|LIA|RSA|LSA|IRP|ILP|SRP
|SLP|IRA|ILA|SRA|SLA|RPI|LPI|RAI|LAI|RPS|LPS|RAS|LAS|PRI|PLI|ARI|ALI
|PRS|PLS|ARS|ALS|IPR|SPR|IAR|SAR|IPL|SPL|IAL|SAL|PIR|PSR|AIR|ASR|PIL
|PSL|AIL|ASL>, --orientation <Axial|Coronal|Sagittal|RIP|LIP|RSP|LSP
|RIA|LIA|RSA|LSA|IRP|ILP|SRP|SLP|IRA|ILA|SRA|SLA|RPI|LPI|RAI|LAI|RPS
|LPS|RAS|LAS|PRI|PLI|ARI|ALI|PRS|PLS|ARS|ALS|IPR|SPR|IAR|SAR|IPL|SPL
|IAL|SAL|PIR|PSR|AIR|ASR|PIL|PSL|AIL|ASL>
Orientation choices (default: LPS)
--, --ignore_rest
Ignores the rest of the labeled arguments following this flag.
--version
Displays version information and exits.
-h, --help
Displays usage information and exits.
<std::string>
(required) Input volume 1
<std::string>
(required) The oriented volume
Description: Orients an output volume. Rearranges the slices in a volume
accoording to the selected orientation. The resulting volume will cover
the original volume.
Author(s): Bill Lorensen
Acknowledgements: This work is part of the National Alliance for Medical
Image Computing (NAMIC), funded by the National Institutes of Health
through the NIH Roadmap for Medical Research, Grant U54 EB005149.
More Information
Acknowledgment
This work is part of the National Alliance for Medical Image Computing (NAMIC), funded by the National Institutes of Health through the NIH Roadmap for Medical Research, Grant U54 EB005149. Information on the National Centers for Biomedical Computing can be obtained from National Centers for Biomedical Computing.