Difference between revisions of "Modules:CurvatureAnisotropicDiffusion-Documentation-3.6"
(Created page with 'Return to Slicer 3.6 Documentation __NOTOC__ ===Module Name=== Curvature Anisotropic Diffusion Filter {| |[[Image:screenshotBlank.png|thumb|280px|Caption …') |
|||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
{| | {| | ||
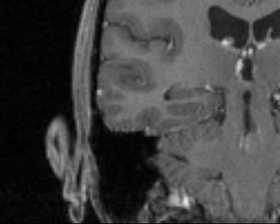
| − | |[[Image: | + | |[[Image:MRIUnfiltered.png|thumb|280px|Unfiltered MRI image]] |
| − | |[[Image: | + | |[[Image:MRICurvatureAnisotropicDiffusion.png|thumb|280px|Curvature filtered with conductance=1 and iterations=10]] |
| − | |||
|} | |} | ||
Latest revision as of 19:51, 28 April 2010
Home < Modules:CurvatureAnisotropicDiffusion-Documentation-3.6Return to Slicer 3.6 Documentation
Module Name
Curvature Anisotropic Diffusion Filter
General Information
Module Type & Category
Type: CLI
Category: Filtering/Denoising
Authors, Collaborators & Contact
- Author: Bill Lorensen
- Contact: bill.lorensen at gmail.com
Module Description
Performs anisotropic diffusion on an image using a modified curvature diffusion equation (MCDE).
MCDE does not exhibit the edge enhancing properties of classic anisotropic diffusion, which can under certain conditions undergo a 'negative' diffusion, which enhances the contrast of edges. Equations of the form of MCDE always undergo positive diffusion, with the conductance term only varying the strength of that diffusion.
Qualitatively, MCDE compares well with other non-linear diffusion techniques. It is less sensitive to contrast than classic Perona-Malik style diffusion, and preserves finer detailed structures in images. There is a potential speed trade-off for using this function in place of Gradient Anisotropic Diffusion. Each iteration of the solution takes roughly twice as long. Fewer iterations, however, may be required to reach an acceptable solution.
Usage
CurvatureAnisotropicDiffusion
[--returnparameterfile
<std::string>]
[--processinformationaddress
<std::string>] [--xml] [--echo]
[--timeStep <double>] [--iterations
<int>] [--conductance <double>]
[--] [--version] [-h] <std::string>
<std::string>
Where:
--returnparameterfile <std::string>
Filename in which to write simple return parameters (int, float,
int-vector, etc.) as opposed to bulk return parameters (image,
geometry, transform, measurement, table).
--processinformationaddress <std::string>
Address of a structure to store process information (progress, abort,
etc.). (default: 0)
--xml
Produce xml description of command line arguments (default: 0)
--echo
Echo the command line arguments (default: 0)
--timeStep <double>
Time Step (default: 0.0625)
--iterations <int>
The more iterations, the more smoothing. Each iteration takes the same
amount of time. If it takes 10 seconds for one iteration, then it will
take 100 seconds for 10 iterations. Note that the conductance controls
how much each iteration smooths across edges. (default: 1)
--conductance <double>
Conductance (default: 1)
--, --ignore_rest
Ignores the rest of the labeled arguments following this flag.
--version
Displays version information and exits.
-h, --help
Displays usage information and exits.
<std::string>
(required) Input volume to be filtered
<std::string>
(required) Output filtered
Development
Source code & documentation
Source Code: CurvatureAnisotropicDiffusion.cxx
XML Description: CurvatureAnisotropicDiffusion.xml
More Information
Acknowledgment
This work is part of the National Alliance for Medical Image Computing (NAMIC), funded by the National Institutes of Health through the NIH Roadmap for Medical Research, Grant U54 EB005149. Information on the National Centers for Biomedical Computing can be obtained from National Centers for Biomedical Computing.