Difference between revisions of "EMSegmenter-Tasks:MRI-Human-Brain"
Belhachemi (talk | contribs) (→Result) |
m (Text replacement - "\[http:\/\/www\.slicer\.org\/slicerWiki\/index\.php\/([^ ]+) ([^]]+)]" to "$2") |
||
| (12 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | [[EMSegmenter-Tasks|Return to EMSegmenter Task Overview Page]] | |
| − | + | =Description= | |
Single channel automatic segmentation of t1w-MRI brain scans into the major tissue classes (gray matter, white matter, csf). The task can only be applied to t1w brain scan showing parts of the skull and neck. The pipeline consist of the following steps: | Single channel automatic segmentation of t1w-MRI brain scans into the major tissue classes (gray matter, white matter, csf). The task can only be applied to t1w brain scan showing parts of the skull and neck. The pipeline consist of the following steps: | ||
| − | * Step 1: Perform image inhomogeneity correction of the MRI scan via [ | + | * Step 1: Perform image inhomogeneity correction of the MRI scan via [[Modules:N4ITKBiasFieldCorrection-Documentation-3.6|N4ITKBiasFieldCorrection]] (Tustison et al 2010) |
| − | * Step 2: Register the atlas to the MRI scan via [[Modules:BRAINSFit| BRAINSFit]] ( | + | * Step 2: Register the atlas to the MRI scan via [[Modules:BRAINSFit| BRAINSFit]] (Johnson et al 2007) |
| − | * Step 3: Compute the intensity distributions for each structure | + | * Step 3: Compute the intensity distributions for each structure <BR> |
| − | * Step 4: Automatically segment the MRI scan into the structures of interest using | + | Compute intensity distribution (mean and variance) for each label by automatically sampling from the MR scan. The sampling for a specific label is constrained to the region that consists of voxels with high probability (top 95%) of being assigned to the label according to the aligned atlas. |
| + | * Step 4: Automatically segment the MRI scan into the structures of interest using [[Modules:EMSegmenter-3.6|EM Algorithm]] (Pohl et al 2007) | ||
| − | + | =Anatomical Tree= | |
* root | * root | ||
| Line 19: | Line 20: | ||
*** cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) | *** cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) | ||
| − | + | =Atlas= | |
| − | Atlas was generated based on 82 scans and corresponding segmentations provided by [http://pnl.bwh.harvard.edu/ Psychiatry Neuroimaging Laboratory, BWH]. We registered the scans to a preselected template via Warfield et al. 2001. | + | Atlas was generated based on 82 scans and corresponding segmentations provided by [http://pnl.bwh.harvard.edu/ Psychiatry Neuroimaging Laboratory, BWH]. We registered the scans to a preselected template via Warfield et al. 2001. <BR> |
Image Dimension = 256 x 256 x 124 <br> | Image Dimension = 256 x 256 x 124 <br> | ||
| − | Image Spacing = 0.9375 x 0.9375 x 1.5 | + | Image Spacing = 0.9375 x 0.9375 x 1.5 <BR> |
| − | = | + | {| class="wikitable" |
| − | [[Image: | + | |- |
| − | [[Image: | + | | [[Image:EMSegmenter_MRI-Human-Brain_Template_420x420.png|210px]] |
| + | | [[Image:EMSegmenter_MRI-Human-Brain_CSF_420x420.png|210px]] | ||
| + | | [[Image:EMSegmenter_MRI-Human-Brain_GM_420x420.png|210px]] | ||
| + | | [[Image:EMSegmenter_MRI-Human-Brain_WM_420x420.png|210px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Template (T1) | ||
| + | | CSF | ||
| + | | GM | ||
| + | | WM | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | ==Acknowledgment | + | =Result= |
| + | <gallery perrow=1: widths=630px : heights=210px> | ||
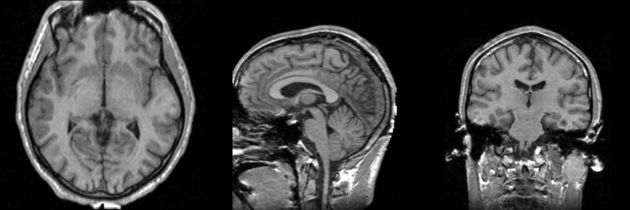
| + | Image:MRI-Human-Brain-T1.png | ||
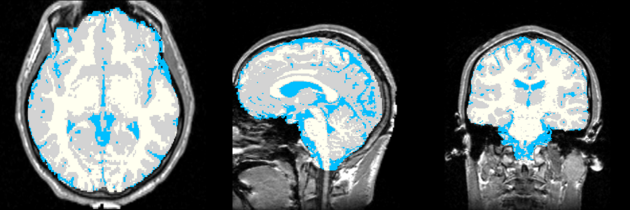
| + | Image:MRI-Human-Brain-Labelmap.png | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Acknowledgment= | ||
The construction of the pipeline was supported by funding from NIH NCRR 2P41RR013218 Supplement. | The construction of the pipeline was supported by funding from NIH NCRR 2P41RR013218 Supplement. | ||
| − | + | =Citations= | |
* Tustison NJ, Avants BB, Cook PA, Zheng Y, Egan A, Yushkevich PA, Gee JC N4ITK: Improved N3 Bias Correction, IEEE Trans Med Imag, 2010 | * Tustison NJ, Avants BB, Cook PA, Zheng Y, Egan A, Yushkevich PA, Gee JC N4ITK: Improved N3 Bias Correction, IEEE Trans Med Imag, 2010 | ||
* Pohl K, Bouix S, Nakamura M, Rohlfing T, McCarley R, Kikinis R, Grimson W, Shenton M, Wells W. [http://www.slicer.org/pages/Special:PubDB_View?dspaceid=608 A Hierarchical Algorithm for MR Brain Image Parcellation.] IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging. 2007 Sept;26(9):1201-1212. | * Pohl K, Bouix S, Nakamura M, Rohlfing T, McCarley R, Kikinis R, Grimson W, Shenton M, Wells W. [http://www.slicer.org/pages/Special:PubDB_View?dspaceid=608 A Hierarchical Algorithm for MR Brain Image Parcellation.] IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging. 2007 Sept;26(9):1201-1212. | ||
* S. Warfield, J. Rexilius, P. Huppi, T. Inder, E. Miller, W. Wells, G. Zientara, F. Jolesz, and R. Kikinis, “A binary entropy measure to assess nonrigid registration algorithms,” in MICCAI, LNCS, pp. 266–274, Springer, October 2001. | * S. Warfield, J. Rexilius, P. Huppi, T. Inder, E. Miller, W. Wells, G. Zientara, F. Jolesz, and R. Kikinis, “A binary entropy measure to assess nonrigid registration algorithms,” in MICCAI, LNCS, pp. 266–274, Springer, October 2001. | ||
| + | * Johnson H.J., Harris G., Williams K. [http://hdl.handle.net/1926/1291 BRAINSFit: Mutual Information Registrations of Whole-Brain 3D Images, Using the Insight Toolkit], The Insight Journal, July 2007 | ||
Latest revision as of 02:29, 27 November 2019
Home < EMSegmenter-Tasks:MRI-Human-BrainReturn to EMSegmenter Task Overview Page
Description
Single channel automatic segmentation of t1w-MRI brain scans into the major tissue classes (gray matter, white matter, csf). The task can only be applied to t1w brain scan showing parts of the skull and neck. The pipeline consist of the following steps:
- Step 1: Perform image inhomogeneity correction of the MRI scan via N4ITKBiasFieldCorrection (Tustison et al 2010)
- Step 2: Register the atlas to the MRI scan via BRAINSFit (Johnson et al 2007)
- Step 3: Compute the intensity distributions for each structure
Compute intensity distribution (mean and variance) for each label by automatically sampling from the MR scan. The sampling for a specific label is constrained to the region that consists of voxels with high probability (top 95%) of being assigned to the label according to the aligned atlas.
- Step 4: Automatically segment the MRI scan into the structures of interest using EM Algorithm (Pohl et al 2007)
Anatomical Tree
- root
- background (BG)
- air (AIR)
- skull (skull)
- intracranial cavity (ICC)
- white matter (WM)
- grey matter (GM)
- cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
- background (BG)
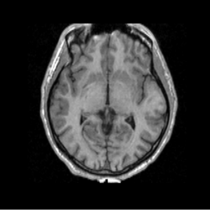
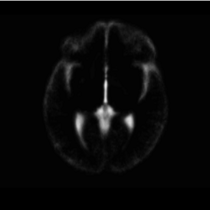
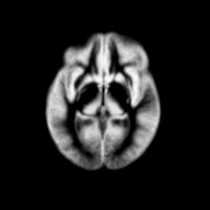
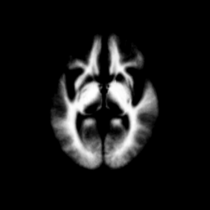
Atlas
Atlas was generated based on 82 scans and corresponding segmentations provided by Psychiatry Neuroimaging Laboratory, BWH. We registered the scans to a preselected template via Warfield et al. 2001.
Image Dimension = 256 x 256 x 124
Image Spacing = 0.9375 x 0.9375 x 1.5
|
|
|
|
| Template (T1) | CSF | GM | WM |
Result
Acknowledgment
The construction of the pipeline was supported by funding from NIH NCRR 2P41RR013218 Supplement.
Citations
- Tustison NJ, Avants BB, Cook PA, Zheng Y, Egan A, Yushkevich PA, Gee JC N4ITK: Improved N3 Bias Correction, IEEE Trans Med Imag, 2010
- Pohl K, Bouix S, Nakamura M, Rohlfing T, McCarley R, Kikinis R, Grimson W, Shenton M, Wells W. A Hierarchical Algorithm for MR Brain Image Parcellation. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging. 2007 Sept;26(9):1201-1212.
- S. Warfield, J. Rexilius, P. Huppi, T. Inder, E. Miller, W. Wells, G. Zientara, F. Jolesz, and R. Kikinis, “A binary entropy measure to assess nonrigid registration algorithms,” in MICCAI, LNCS, pp. 266–274, Springer, October 2001.
- Johnson H.J., Harris G., Williams K. BRAINSFit: Mutual Information Registrations of Whole-Brain 3D Images, Using the Insight Toolkit, The Insight Journal, July 2007