Difference between revisions of "Modules:HistogramMatching-Documentation-3.6"
m |
|||
| (10 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
{| | {| | ||
| − | |[[Image:HistogramMatching1.png|thumb| | + | |[[Image:HistogramMatching-3-6.png|thumb|240px|Histogram Matching UI]] |
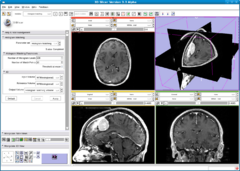
| − | |[[Image:HistogramMatching2.png|thumb| | + | |[[Image:HistogramMatching1.png|thumb|240px|Reference image: MR Acquisition 1]] |
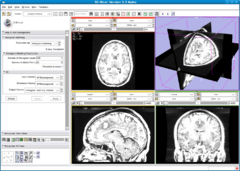
| − | |[[Image:HistogramMatching3.png|thumb| | + | |[[Image:HistogramMatching2.png|thumb|240px|Source image: MR Acquisition 2 ]] |
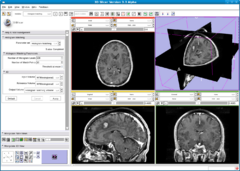
| + | |[[Image:HistogramMatching3.png|thumb|240px|Output image: MR Acquisition 2 matched to MR Acquisition 1]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 42: | Line 43: | ||
===Examples, Use cases & Tutorials=== | ===Examples, Use cases & Tutorials=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The filter was orginally designed to normalize MR images of the same MR protocol and same body part. The algorithm works best if background pixels are excluded from both the source and reference histograms. | ||
| + | |||
| + | A command line example is: | ||
| + | |||
| + | HistogramMatching --numberOfHistogramLevels 64 | ||
| + | --numberOfMatchPoints 10 | ||
| + | ${TEST_DATA}/CTHeadAxial.nhdr | ||
| + | ${TEST_DATA}/MRHeadResampled.nhdr | ||
| + | ${TEMP}/HistogramMatchingTest.nhdr | ||
===Quick Tour of Features and Use=== | ===Quick Tour of Features and Use=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Input/Output panel | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:HistogramMatching-IOPanels-3-6.png|thumb|right|280px|Input/Output panels]] | ||
| + | The module takes two input volumes and generate one output volume. The '''Input Volume''' is the volume whose histogram is to be transformed. The '''Reference Volume''' is a volume that provide a target histogram for the first volume. Upon completion of execution, the result is stored in the '''Output Volume'''. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Parameters panel | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:HistogramMatching-ParametersPanels-3-6.png|thumb|right|280px|Parameters panels]] | ||
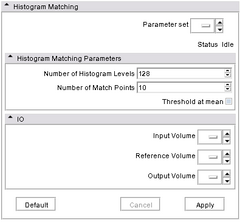
| + | The user can specify parameters for the histogram module on this panel. The '''Number of Histogram Level''' specifies how many levels the intensity range is divided. The '''Number of Matching Points''' tells the module the number of quantile points in the histogram to be matched. When '''Threshold at mean''' is checked, the module will exclude background voxels from the histogram matching process. | ||
==Development== | ==Development== | ||
| Line 56: | Line 77: | ||
===Usability Issues=== | ===Usability Issues=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Source Code and Documentation=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Source Code: [http://www.na-mic.org/ViewVC/index.cgi/trunk/Applications/CLI/HistogramMatching.cxx?view=co HistogramMatching.cxx] | ||
| + | |||
| + | XML Description: [http://www.na-mic.org/ViewVC/index.cgi/trunk/Applications/CLI/HistogramMatching.xml?view=co HistogramMatching.xml] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Test: [http://viewvc.na-mic.org/viewcvs.cgi/trunk/Applications/CLI/Testing/HistogramMatchingTest.cxx?rev=11537&view=log HistogramMatchingTest.cxx] | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
| Line 107: | Line 136: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| − | == | + | ==More Information== |
| − | === | + | ===Acknowledgement=== |
| + | This work is part of the National Alliance for Medical Image Computing (NAMIC), funded by the National Institutes of Health through the NIH Roadmap for Medical Research, Grant U54 EB005149. | ||
| − | + | ===References=== | |
| − | + | Internally, the module uses itk::HistogramMatchingImageFilter. More details on algorithm can be found [http://public.kitware.com/Insight/Doxygen/html/classitk_1_1HistogramMatchingImageFilter.html here]. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 03:27, 29 April 2010
Home < Modules:HistogramMatching-Documentation-3.6Return to Slicer 3.6 Documentation
Module Name
Histogram Matching
General Information
Module Type & Category
Type: CLI
Category: Filtering
Authors, Collaborators & Contact
- Author: Bill Lorensen
- Contact: bill.lorensen at gmail.com
Module Description
Normalizes the grayscale values of a source image based on the grayscale values of a reference image. This filter uses a histogram matching technique where the histograms of the two images are matched only at a specified number of quantile values. The filter was orginally designed to normalize MR images of the same MR protocol and same body part. The algorithm works best if background pixels are excluded from both the source and reference histograms. A simple background exclusion method is to exclude all pixels whose grayscale values are smaller than the mean grayscale value. ThresholdAtMeanIntensity switches on this simple background exclusion method. Number of match points governs the number of quantile values to be matched. The filter assumes that both the source and reference are of the same type and that the input and output image type have the same number of dimension and have scalar pixel types.
Usage
Examples, Use cases & Tutorials
The filter was orginally designed to normalize MR images of the same MR protocol and same body part. The algorithm works best if background pixels are excluded from both the source and reference histograms.
A command line example is:
HistogramMatching --numberOfHistogramLevels 64
--numberOfMatchPoints 10
${TEST_DATA}/CTHeadAxial.nhdr
${TEST_DATA}/MRHeadResampled.nhdr
${TEMP}/HistogramMatchingTest.nhdr
Quick Tour of Features and Use
- Input/Output panel
The module takes two input volumes and generate one output volume. The Input Volume is the volume whose histogram is to be transformed. The Reference Volume is a volume that provide a target histogram for the first volume. Upon completion of execution, the result is stored in the Output Volume.
- Parameters panel
The user can specify parameters for the histogram module on this panel. The Number of Histogram Level specifies how many levels the intensity range is divided. The Number of Matching Points tells the module the number of quantile points in the histogram to be matched. When Threshold at mean is checked, the module will exclude background voxels from the histogram matching process.
Development
Dependencies
Depends only on the core IO and display functionalities of Slicer.
Known Bugs
None.
Usability Issues
Source Code and Documentation
Source Code: HistogramMatching.cxx
XML Description: HistogramMatching.xml
Test: HistogramMatchingTest.cxx
./HistogramMatching [--processinformationaddress <std::string>] [--xml]
[--echo] [--threshold] [--numberOfMatchPoints
<int>] [--numberOfHistogramLevels <int>] [--]
[--version] [-h] <std::string> <std::string>
<std::string>
Where:
--processinformationaddress <std::string>
Address of a structure to store process information (progress, abort,
etc.). (default: 0)
--xml
Produce xml description of command line arguments (default: 0)
--echo
Echo the command line arguments (default: 0)
--threshold
If on, only pixels above the mean in each volume are thresholded.
(default: 0)
--numberOfMatchPoints <int>
The number of match points to use (default: 10)
--numberOfHistogramLevels <int>
The number of hisogram levels to use (default: 128)
--, --ignore_rest
Ignores the rest of the labeled arguments following this flag.
--version
Displays version information and exits.
-h, --help
Displays usage information and exits.
<std::string>
(required) Input volume to be filtered
<std::string>
(required) Input volume whose histogram will be matched
<std::string>
(required) Output volume. This is the input volume with intensities
matched to the reference volume.
More Information
Acknowledgement
This work is part of the National Alliance for Medical Image Computing (NAMIC), funded by the National Institutes of Health through the NIH Roadmap for Medical Research, Grant U54 EB005149.
References
Internally, the module uses itk::HistogramMatchingImageFilter. More details on algorithm can be found here.